Functions and Their Notation
4.1 Learning Objectives
- Define a function using tables
- Define a function from a set of ordered pairs
- Define the domain and range of a function given as a table or a set of ordered pairs
- Write functions using algebraic notation
- Use the vertical line test to determine whether a graph represents a function
- Given a function described by an equation, find function values (outputs) for numerical inputs
- Given a function described by an equation, find function values (outputs) for variable inputs
| Family Member's Name (Input) | Family Member's Age |
|---|---|
| Nellie | 13 |
| Marcos | 11 |
| Esther | 46 |
| Samuel | 47 |
| Nina | 47 |
| Paul | 47 |
| Katrina | 21 |
| Andrew | 16 |
| Maria | 13 |
| Ana | 81 |
| Starting Information (Input) Family Member’s Age | Related Information (Output) Family Member’s Name |
|---|---|
| 11 | Marcos |
| 13 | Nellie Maria |
| 16 | Andrew |
| 21 | Katrina |
| 46 | Esther |
| 47 | Samuel Nina Paul |
| 81 | Ana |
Example 4.1.A
Fill in the table.| Input | Output | Function? | Why or why not? |
|---|---|---|---|
| Name of senator | Name of state | ||
| Name of state | Name of senator | ||
| Time elapsed | Height of a tossed ball | ||
| Height of a tossed ball | Time elapsed | ||
| Number of cars | Number of tires | ||
| Number of tires | Number of cars |
Answer:
| Input | Output | Function? | Why or why not? |
|---|---|---|---|
| Name of senator | Name of state | Yes | For each input, there will only be one output because a senator only represents one state. |
| Name of state | Name of senator | No | For each state that is an input, 2 names of senators would result because each state has two senators. |
| Time elapsed | Height of a tossed ball | Yes | At a specific time, the ball has one specific height. |
| Height of a tossed ball | Time elapsed | No | Remember that the ball was tossed up and fell down. So for a given height, there could be two different times when the ball was at that height. The input height can result in more than one output. |
| Number of cars | Number of tires | Yes | For any input of a specific number of cars, there is one specific output representing the number of tires. |
| Number of tires | Number of cars | Yes | For any input of a specific number of tires, there is one specific output representing the number of cars. |
Example 4.1.B
List the domain and range for the following table of values where x is the input and y is the output.| x | y |
|---|---|
| [latex]−3[/latex] | [latex]4[/latex] |
| [latex]−2[/latex] | [latex]4[/latex] |
| [latex]−1[/latex] | [latex]4[/latex] |
| [latex]2[/latex] | [latex]4[/latex] |
| [latex]3[/latex] | [latex]4[/latex] |
Answer: The domain describes all the inputs, and we can use set notation with brackets{} to make the list. [latex-display]\text{Domain}:\{-3,-2,-1,2,3\}\\[/latex-display] The range describes all the outputs. [latex-display]\text{Range}:\{4\}\\[/latex-display] We only listed 4 once because it is not necessary to list it every time it appears in the range.
Example 4.1.C
Define the domain and range for the following set of ordered pairs, and determine whether the relation given is a function.[latex]\{(−3,−6),(−2,−1),(1,0),(1,5),(2,0)\}[/latex]
Answer: We list all of the input values as the domain. The input values are represented first in the ordered pair as a matter of convention. Domain: {-3,-2,1,2} Note how we didn't enter repeated values more than once, it is not necessary. The range is the list of outputs for the relation, they are entered second in the ordered pair. Range: {-6, -1, 0, 5} Organizing the ordered pairs in a table can help you tell whether this relation is a function. By definition, the inputs in a function have only one output.
| x | y |
|---|---|
| [latex]−3[/latex] | [latex]−6[/latex] |
| [latex]−2[/latex] | [latex]−1[/latex] |
| [latex]1[/latex] | [latex]0[/latex] |
| [latex]1[/latex] | [latex]5[/latex] |
| [latex]2[/latex] | [latex]0[/latex] |
Answer
Domain: {-3,-2,1,2} Range: {-6, -1, 0, 5} The relation is not a function because the input 1 has two outputs: 0 and 5.Example 4.1.D
Define the domain and range of this relation and determine whether it is a function.[latex]\{(−3, 4),(−2, 4),( −1, 4),(2, 4),(3, 4)\}[/latex]
Answer: Domain: {-3, -2, -1, 2, 3} Range: {4} To help you determine whether this is a function, you could reorganize the information by creating a table.
| x | y |
|---|---|
| [latex]−3[/latex] | [latex]4[/latex] |
| [latex]−2[/latex] | [latex]4[/latex] |
| [latex]−1[/latex] | [latex]4[/latex] |
| [latex]2[/latex] | [latex]4[/latex] |
| [latex]3[/latex] | [latex]4[/latex] |
Answer
Domain: {-3, -2, -1, 2, 3} Range: {4} This relation is a function.4.1.1 Using Function Notation
Once we determine that a relationship is a function, we need to display and define the functional relationships so that we can understand and use them, and sometimes also so that we can program them into computers. There are various ways of representing functions. A standard function notation is one representation that facilitates working with functions. Now you try it.Example 4.1.E
Represent height as a function of age using function notation.Answer: To represent "height is a function of age," we start by identifying the descriptive variables [latex]h[/latex] for height and [latex]a[/latex] for age. [latex-display]\begin{array}{ccc}h\text{ is }f\text{ of }a\hfill & \hfill & \hfill & \hfill & \text{We name the function }f;\text{ height is a function of age}.\hfill \\ h=f\left(a\right)\hfill & \hfill & \hfill & \hfill & \text{We use parentheses to indicate the function input}\text{. }\hfill \\ f\left(a\right)\hfill & \hfill & \hfill & \hfill & \text{We name the function }f;\text{ the expression is read as ''}f\text{ of }a\text{.''}\hfill \end{array}[/latex-display]
Analysis of the solution
We can use any letter to name the function; the notation [latex]h\left(a\right)[/latex] shows us that [latex]h[/latex] depends on [latex]a[/latex]. The value [latex]a[/latex] must be put into the function [latex]h[/latex] to get a result. The parentheses indicate that age is input into the function; they do not indicate multiplication. Let's try another.Example 4.1.F
- Write the formula for perimeter of a square, [latex]P=4s[/latex], as a function.
- Write the formula for area of a square, [latex]A=l^{2}[/latex], as a function.
Answer:
- Name the function P. P is a function of the length of the sides, s. Perimeter as a function of side length is equal to 4 times side length. [latex]P(s)=4s[/latex]
- Name the function A. Area as a function of the length of the sides is equal to the length squared.[latex]A(l)=l^{2}[/latex].
A General Note: Function Notation
The notation [latex]y=f\left(x\right)[/latex] defines a function named [latex]f[/latex]. This is read as "[latex]y[/latex] is a function of [latex]x[/latex]." The letter [latex]x[/latex] represents the input value, or independent variable. The letter y or [latex]f\left(x\right)[/latex], represents the output value, or dependent variable.Example 4.1.G
Use function notation to represent a function whose input is the name of a month and output is the number of days in that month.Answer: The number of days in a month is a function of the name of the month, so if we name the function [latex]f[/latex], we write [latex]\text{days}=f\left(\text{month}\right)[/latex] or [latex]d=f\left(m\right)[/latex]. The name of the month is the input to a "rule" that associates a specific number (the output) with each input.
 For example, [latex]f\left(\text{March}\right)=31[/latex], because March has 31 days. The notation [latex]d=f\left(m\right)[/latex] reminds us that the number of days, [latex]d[/latex] (the output), is dependent on the name of the month, [latex]m[/latex] (the input).
For example, [latex]f\left(\text{March}\right)=31[/latex], because March has 31 days. The notation [latex]d=f\left(m\right)[/latex] reminds us that the number of days, [latex]d[/latex] (the output), is dependent on the name of the month, [latex]m[/latex] (the input).
Example 4.1.H
A function [latex]N=f\left(y\right)[/latex] gives the number of police officers, [latex]N[/latex], in a town in year [latex]y[/latex]. What does [latex]f\left(2005\right)=300[/latex] represent?Answer: When we read [latex]f\left(2005\right)=300[/latex], we see that the input year is 2005. The value for the output, the number of police officers [latex]\left(N\right)[/latex], is 300. Remember, [latex]N=f\left(y\right)[/latex]. The statement [latex]f\left(2005\right)=300[/latex] tells us that in the year 2005 there were 300 police officers in the town.
4.1.2 Graphs of functions
When both the independent quantity (input) and the dependent quantity (output) are real numbers, a function can be represented by a graph in the coordinate plane. The independent value is plotted on the x-axis and the dependent value is plotted on the y-axis. The fact that each input value has exactly one output value means graphs of functions have certain characteristics. For each input on the graph, there will be exactly one output. For a function defined as y = f(x), or y is a function of x, we would write ordered pairs (x, f(x)) using function notation instead of (x,y) as you may have seen previously. We can identify whether the graph of a relation represents a function because for each x-coordinate there will be exactly one y-coordinate.
We can identify whether the graph of a relation represents a function because for each x-coordinate there will be exactly one y-coordinate.
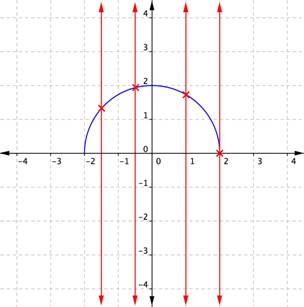
Example 4.1.I
Use the vertical line test to determine whether the relation plotted on this graph is a function.
Answer: This relationship cannot be a function, because some of the x-coordinates have two corresponding y-coordinates.

Example 4.1.J
Consider the ordered pairs [latex]\{(−1,3),(−2,5),(−3,3),(−5,−3)\}[/latex], plotted on the graph below. Use the vertical line test to determine whether the set of ordered pairs represents a function.
Answer:
Drawing vertical lines through each point results in each line only touching one point. This means that none of the x-coordinates have two corresponding y-coordinates, so this is a function.

4.1.3 Evaluate Functions
Throughout this course, you have been working with algebraic equations. Many of these equations are functions. For example, [latex]y=4x+1[/latex] is an equation that can also represent a function. When you input values for x, you can determine a single output for y. In this case, if you substitute [latex]x=10[/latex] into the equation you will find that y must be 41; there is no other value of y that would make the equation true. Rather than using the variable y, the equations of functions can be written using function notation. Function notation is very useful when you are working with more than one function at a time, and substituting more than one variable in for x. Equations written using function notation can also be evaluated. With function notation, you might see a problem like this. Given [latex]f(x)=4x+1[/latex], find f(2). You read this problem like this: “given f of x equals 4x plus one, find f of 2.” While the notation and wording is different, the process of evaluating a function is the same as evaluating an equation: in both cases, you substitute 2 for x, multiply it by 4 and add 1, simplifying to get 9. In both a function and an equation, an input of 2 results in an output of 9.[latex]f(x)=4x+1\\f(2)=4(2)+1=8+1=9[/latex]
You can simply apply what you already know about evaluating expressions to evaluate a function. It’s important to note that the parentheses that are part of function notation do not mean multiply. The notation f(x) does not mean f multiplied by x. Instead the notation means “f of x” or “the function of x” To evaluate the function, take the value given for x, and substitute that value in for x in the expression. Let’s look at a couple of examples.Example 4.1.K
Given [latex]f(x)=3x–4[/latex], find f(5).Answer: Substitute 5 in for x in the function.
[latex]f(5)=3(5)-4[/latex]
Simplify the expression on the right side of the equation.[latex]f(5)=15-4\\f(5)=11[/latex]
Answer
Given [latex]f(x)=3x–4[/latex], [latex]f(5)=11[/latex].Example 4.1.L
Given [latex]p(x)=2x^{2}+5[/latex], find [latex]p(−3)[/latex].Answer: Substitute [latex]-3[/latex] in for x in the function.
[latex]p(−3)=2(−3)^{2}+5[/latex]
Simplify the expression on the right side of the equation.[latex]p(−3)=2(9)+5\\p(−3)=18+5\\p(−3)=23[/latex]
Answer
Given [latex]p(x)=2x^{2}+5[/latex], [latex]p(−3)=23[/latex].Example 4.1.M
Given [latex]f(x)=|4x-3|[/latex], find [latex]f(0)[/latex], [latex]f(2)[/latex], and [latex]f(−1)[/latex].Answer: Treat each of these like three separate problems. In each case, you substitute the value in for x and simplify. Start with [latex]x=0[/latex].
[latex]f(0)=|4(0)-3|\\=|-3|\\f(0)=3[/latex]
Evaluate for [latex]x=2[/latex].[latex]f(2)=|4(2)-3|\\=|5|\\f(2)=5[/latex]
Evaluate for [latex]x=−1[/latex].[latex]f(−1)=|4(-1)-3|\\=|-7|\\f(-1)=7[/latex]
Answer
Given [latex]f(x)=|4x-3|[/latex], [latex]f(0)=3[/latex], [latex]f(2)=5[/latex], and [latex]f(‒1)=7[/latex].4.1.4 Variable Inputs
So far, you have evaluated functions for inputs that have been constants. Functions can also be evaluated for inputs that are variables or expressions. The process is the same, but the simplified answer will contain a variable. The following examples show how to evaluate a function for a variable input.Example 4.1.N
Given [latex]f(x)=3x^{2}+2x+1[/latex], find f(b).Answer: This problem is asking you to evaluate the function for b. This means substitute b in the equation for x. [latex-display]f(b)=3b^{2}+2b+1[/latex-display] (That’s it—you’re done.)
Answer
Given [latex]f(x)=3x^{2}+2x+1[/latex], [latex]f(b)=3b^{2}+2b+1[/latex].Example 4.1.O
Given [latex]f(x)=4x+1[/latex], find [latex]f(h+1)[/latex].Answer: This time, you substitute [latex](h+1)[/latex] into the equation for x. [latex]f(h+1)=4(h+1)+1[/latex] Use the distributive property on the right side, and then combine like terms to simplify. [latex-display]f(h+1)=4h+4+1=4h+5[/latex-display]
Answer
Given [latex]f(x)=4x+1[/latex], [latex]f(h+1)=4h+5[/latex].Summary
- Identify the input values - this is your domain.
- Identify the output values - this is your range.
- If each value in the domain leads to only one value in the range, classify the relationship as a function. If any value in the domain leads to two or more values in the range, do not classify the relationship as a function.
Licenses & Attributions
CC licensed content, Original
- Revision and Adaptation. Provided by: Lumen Learning License: CC BY: Attribution.
- Revision and Adaptation. Provided by: Lumen Learning License: CC BY: Attribution.
- Revision and Adaptation. Provided by: Lumen Learning License: CC BY: Attribution.
CC licensed content, Shared previously
- Ex 1: Find Domain and Range of Ordered Pairs, Function or Not. Authored by: James Sousa (Mathispower4u.com) . License: CC BY: Attribution.
- College Algebra. Provided by: OpenStax Located at: https://cnx.org/contents/[email protected]:1/Preface.. License: CC BY: Attribution.
- Ex: Give the Domain and Range Given the Points in a Table. Authored by: James Sousa (Mathispower4u.com) . License: CC BY: Attribution.
- Ex: Determine if a Table of Values Represents a Function. Authored by: James Sousa (Mathispower4u.com) . License: CC BY: Attribution.
- Ex: Function Notation Application Problem. Authored by: James Sousa (Mathispower4u.com) . License: CC BY: Attribution.
- Function Notation Application. Authored by: James Sousa (Mathispower4u.com) . License: CC BY: Attribution.
- College Algebra. Provided by: OpenStax Located at: https://cnx.org/contents/[email protected]:1/Preface. License: CC BY: Attribution. License terms: Download for free at : http://cnx.org/contents/[email protected]:1/Preface.
- Ex: Determine if a Table of Values Represents a Function. Authored by: James Sousa (Mathispower4u.com) . License: CC BY: Attribution.
- Ex: Determine Various Function Outputs for a Quadratic Function. Authored by: James Sousa (Mathispower4u.com) . License: CC BY: Attribution.
