Characteristics of Inverse Functions
Learning Outcomes
- Identify an inverse for tabular data.
- Test whether two functions are inverses.
- Determine the domain and range of an inverse.
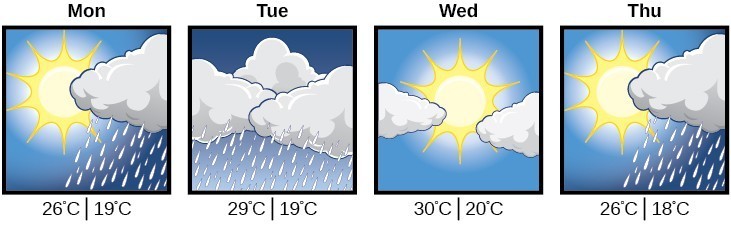 Knowing that a comfortable 75 degrees Fahrenheit is about 24 degrees Celsius, he sends his assistant the week’s weather forecast for Milan, and asks her to convert all of the temperatures to degrees Fahrenheit.
At first, Betty considers using the formula she has already found to complete the conversions. After all, she knows her algebra, and can easily solve the equation for [latex]F[/latex] after substituting a value for [latex]C[/latex]. For example, to convert 26 degrees Celsius, she could write
Knowing that a comfortable 75 degrees Fahrenheit is about 24 degrees Celsius, he sends his assistant the week’s weather forecast for Milan, and asks her to convert all of the temperatures to degrees Fahrenheit.
At first, Betty considers using the formula she has already found to complete the conversions. After all, she knows her algebra, and can easily solve the equation for [latex]F[/latex] after substituting a value for [latex]C[/latex]. For example, to convert 26 degrees Celsius, she could write
[latex]\begin{align}&26=\frac{5}{9}\left(F - 32\right) \\[1.5mm] &26\cdot \frac{9}{5}=F - 32 \\[1.5mm] &F=26\cdot \frac{9}{5}+32\approx 79 \end{align}[/latex]
After considering this option for a moment, however, she realizes that solving the equation for each of the temperatures will be awfully tedious. She realizes that since evaluation is easier than solving, it would be much more convenient to have a different formula, one that takes the Celsius temperature and outputs the Fahrenheit temperature. The formula for which Betty is searching corresponds to the idea of an inverse function, which is a function for which the input of the original function becomes the output of the inverse function and the output of the original function becomes the input of the inverse function. Given a function [latex]f\left(x\right)[/latex], we represent its inverse as [latex]{f}^{-1}\left(x\right)[/latex], read as "[latex]f[/latex] inverse of [latex]x[/latex]." The raised [latex]-1[/latex] is part of the notation. It is not an exponent; it does not imply a power of [latex]-1[/latex] . In other words, [latex]{f}^{-1}\left(x\right)[/latex] does not mean [latex]\frac{1}{f\left(x\right)}[/latex] because [latex]\frac{1}{f\left(x\right)}[/latex] is the reciprocal of [latex]f[/latex] and not the inverse. The "exponent-like" notation comes from an analogy between function composition and multiplication: just as [latex]{a}^{-1}a=1[/latex] (1 is the identity element for multiplication) for any nonzero number [latex]a[/latex], so [latex]{f}^{-1}\circ f[/latex] equals the identity function, that is,[latex]\left({f}^{-1}\circ f\right)\left(x\right)={f}^{-1}\left(f\left(x\right)\right)={f}^{-1}\left(y\right)=x[/latex]
This holds for all [latex]x[/latex] in the domain of [latex]f[/latex]. Informally, this means that inverse functions "undo" each other. However, just as zero does not have a reciprocal, some functions do not have inverses that are also functions. Given a function [latex]f\left(x\right)[/latex], we can verify whether some other function [latex]g\left(x\right)[/latex] is the inverse of [latex]f\left(x\right)[/latex] by checking whether either [latex]g\left(f\left(x\right)\right)=x[/latex] or [latex]f\left(g\left(x\right)\right)=x[/latex] is true. We can test whichever equation is more convenient to work with because they are logically equivalent (that is, if one is true, then so is the other.) For example, [latex]y=4x[/latex] and [latex]y=\frac{1}{4}x[/latex] are inverse functions.[latex]\left({f}^{-1}\circ f\right)\left(x\right)={f}^{-1}\left(4x\right)=\frac{1}{4}\left(4x\right)=x[/latex]
and[latex]\left({f}^{}\circ {f}^{-1}\right)\left(x\right)=f\left(\frac{1}{4}x\right)=4\left(\frac{1}{4}x\right)=x[/latex]
A few coordinate pairs from the graph of the function [latex]y=4x[/latex] are (−2, −8), (0, 0), and (2, 8). A few coordinate pairs from the graph of the function [latex]y=\frac{1}{4}x[/latex] are (−8, −2), (0, 0), and (8, 2). If we interchange the input and output of each coordinate pair of a function, the interchanged coordinate pairs would appear on the graph of the inverse function.A General Note: Inverse Function
For any one-to-one function [latex]f\left(x\right)=y[/latex], a function [latex]{f}^{-1}\left(x\right)[/latex] is an inverse function of [latex]f[/latex] if [latex]{f}^{-1}\left(y\right)=x[/latex]. This can also be written as [latex]{f}^{-1}\left(f\left(x\right)\right)=x[/latex] for all [latex]x[/latex] in the domain of [latex]f[/latex]. It also follows that [latex]f\left({f}^{-1}\left(x\right)\right)=x[/latex] for all [latex]x[/latex] in the domain of [latex]{f}^{-1}[/latex] if [latex]{f}^{-1}[/latex] is the inverse of [latex]f[/latex]. The notation [latex]{f}^{-1}[/latex] is read "[latex]f[/latex] inverse." Like any other function, we can use any variable name as the input for [latex]{f}^{-1}[/latex], so we will often write [latex]{f}^{-1}\left(x\right)[/latex], which we read as [latex]"f[/latex] inverse of [latex]x[/latex]". Keep in mind that [latex]{f}^{-1}\left(x\right)\ne \frac{1}{f\left(x\right)}[/latex] and not all functions have inverses.tip for success
The note in the box above cannot be taken too lightly. It's worth another read to be sure you understand the notation. As with all difficult concepts, it's perfectly natural to take some time before you understand it. Working the examples in the text section on paper will help.Example: Identifying an Inverse Function for a Given Input-Output Pair
If for a particular one-to-one function [latex]f\left(2\right)=4[/latex] and [latex]f\left(5\right)=12[/latex], what are the corresponding input and output values for the inverse function?Answer: The inverse function reverses the input and output quantities, so if
[latex]f\left(2\right)=4[/latex], then [latex]{f}^{-1}\left(4\right)=2[/latex]
and if
[latex]f\left(5\right)=12[/latex], then [latex]{f}^{-1}\left(12\right)=5[/latex]
Alternatively, if we want to name the inverse function [latex]g[/latex], then [latex]g\left(4\right)=2[/latex] and [latex]g\left(12\right)=5[/latex].Analysis of the Solution
Notice that if we show the coordinate pairs in a table form, the input and output are clearly reversed.| [latex]\left(x,f\left(x\right)\right)[/latex] | [latex]\left(x,g\left(x\right)\right)[/latex] |
|---|---|
| [latex]\left(2,4\right)[/latex] | [latex]\left(4,2\right)[/latex] |
| [latex]\left(5,12\right)[/latex] | [latex]\left(12,5\right)[/latex] |
Try It
Given that [latex]{h}^{-1}\left(6\right)=2[/latex], what are the corresponding input and output values of the original function [latex]h?[/latex]Answer: [latex-display]h(2)=6[/latex-display]
How To: Given two functions [latex]f\left(x\right)[/latex] and [latex]g\left(x\right)[/latex], test whether the functions are inverses of each other.
- Determine whether [latex]f\left(g\left(x\right)\right)=x[/latex] and [latex]g\left(f\left(x\right)\right)=x[/latex].
- If both statements are true, then [latex]g={f}^{-1}[/latex] and [latex]f={g}^{-1}[/latex]. If either statement is false, then [latex]g\ne {f}^{-1}[/latex] and [latex]f\ne {g}^{-1}[/latex].
Example: Testing Inverse Relationships Algebraically
If [latex]f\left(x\right)=\dfrac{1}{x+2}[/latex] and [latex]g\left(x\right)=\dfrac{1}{x}-2[/latex], is [latex]g={f}^{-1}?[/latex]Answer:
[latex]\begin{align} g\left(f\left(x\right)\right)&=\frac{1}{\left(\frac{1}{x+2}\right)}{-2 }\\[1.5mm]&={ x }+{ 2 } -{ 2 }\\[1.5mm]&={ x } \end{align}[/latex]
so[latex]g={f}^{-1}\text{ and }f={g}^{-1}[/latex]
This is enough to answer yes to the question, but we can also verify the other formula.[latex]\begin{align} f\left(g\left(x\right)\right)&=\frac{1}{\frac{1}{x}-2+2}\\[1.5mm] &=\frac{1}{\frac{1}{x}} \\[1.5mm] &=x \end{align}[/latex]
Analysis of the Solution
Notice the inverse operations are in reverse order of the operations from the original function.Try It
If [latex]f\left(x\right)={x}^{3}-4[/latex] and [latex]g\left(x\right)=\sqrt[3]{x+4}[/latex], is [latex]g={f}^{-1}?[/latex]Answer: Yes
Example: Determining Inverse Relationships for Power Functions
If [latex]f\left(x\right)={x}^{3}[/latex] (the cube function) and [latex]g\left(x\right)=\frac{1}{3}x[/latex], is [latex]g={f}^{-1}?[/latex]Answer: [latex-display]f\left(g\left(x\right)\right)=\left(\frac{1}{3}x\right)^3=\dfrac{{x}^{3}}{27}\ne x[/latex-display] No, the functions are not inverses.
Analysis of the Solution
The correct inverse to [latex]x^3[/latex] is the cube root [latex]\sqrt[3]{x}={x}^{\frac{1}{3}}[/latex], that is, the one-third is an exponent, not a multiplier.Try It
If [latex]f\left(x\right)={\left(x - 1\right)}^{3}\text{and}g\left(x\right)=\sqrt[3]{x}+1[/latex], is [latex]g={f}^{-1}?[/latex]Answer: Yes
Determine the Domain and Range of an Inverse Function
The outputs of the function [latex]f[/latex] are the inputs to [latex]{f}^{-1}[/latex], so the range of [latex]f[/latex] is also the domain of [latex]{f}^{-1}[/latex]. Likewise, because the inputs to [latex]f[/latex] are the outputs of [latex]{f}^{-1}[/latex], the domain of [latex]f[/latex] is the range of [latex]{f}^{-1}[/latex]. We can visualize the situation.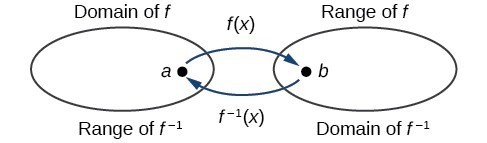 Domain and range of a function and its inverse
Domain and range of a function and its inverse- The domain of [latex]f[/latex] = range of [latex]{f}^{-1}[/latex] = [latex]\left[1,\infty \right)[/latex].
- The domain of [latex]{f}^{-1}[/latex] = range of [latex]f[/latex] = [latex]\left[0,\infty \right)[/latex].
A General Note: Domain and Range of Inverse Functions
The range of a function [latex]f\left(x\right)[/latex] is the domain of the inverse function [latex]{f}^{-1}\left(x\right)[/latex]. The domain of [latex]f\left(x\right)[/latex] is the range of [latex]{f}^{-1}\left(x\right)[/latex].How To: Given a function, find the domain and range of its inverse.
- If the function is one-to-one, write the range of the original function as the domain of the inverse, and write the domain of the original function as the range of the inverse.
- If the domain of the original function needs to be restricted to make it one-to-one, then this restricted domain becomes the range of the inverse function.
Example: Finding the Inverses of Toolkit Functions
Identify which of the toolkit functions besides the quadratic function are not one-to-one, and find a restricted domain on which each function is one-to-one, if any. The toolkit functions are reviewed below. We restrict the domain in such a fashion that the function assumes all y-values exactly once.| Constant | Identity | Quadratic | Cubic | Reciprocal |
| [latex]f\left(x\right)=c[/latex] | [latex]f\left(x\right)=x[/latex] | [latex]f\left(x\right)={x}^{2}[/latex] | [latex]f\left(x\right)={x}^{3}[/latex] | [latex]f\left(x\right)=\frac{1}{x}[/latex] |
| Reciprocal squared | Cube root | Square root | Absolute value | |
| [latex]f\left(x\right)=\frac{1}{{x}^{2}}[/latex] | [latex]f\left(x\right)=\sqrt[3]{x}[/latex] | [latex]f\left(x\right)=\sqrt{x}[/latex] | [latex]f\left(x\right)=|x|[/latex] |
Answer: The constant function is not one-to-one, and there is no domain (except a single point) on which it could be one-to-one, so the constant function has no meaningful inverse. The absolute value function can be restricted to the domain [latex]\left[0,\infty \right)[/latex], where it is equal to the identity function. The reciprocal-squared function can be restricted to the domain [latex]\left(0,\infty \right)[/latex].
Analysis of the Solution
We can see that these functions (if unrestricted) are not one-to-one by looking at their graphs. They both would fail the horizontal line test. However, if a function is restricted to a certain domain so that it passes the horizontal line test, then in that restricted domain, it can have an inverse.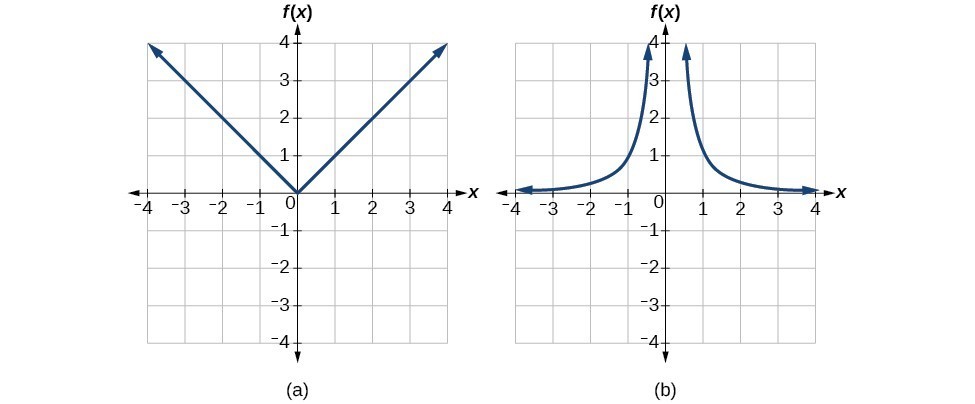 (a) Absolute value (b) Reciprocal squared
(a) Absolute value (b) Reciprocal squaredTry It
The domain of the function [latex]f[/latex] is [latex]\left(1,\infty \right)[/latex] and the range of the function [latex]f[/latex] is [latex]\left(\mathrm{-\infty },-2\right)[/latex]. Find the domain and range of the inverse function.Answer: The domain of the function [latex]{f}^{-1}[/latex] is [latex]\left(-\infty \text{,}-2\right)[/latex] and the range of the function [latex]{f}^{-1}[/latex] is [latex]\left(1,\infty \right)[/latex].
Licenses & Attributions
CC licensed content, Original
- Revision and Adaptation. Provided by: Lumen Learning License: CC BY: Attribution.
CC licensed content, Shared previously
- Ex: Find an Inverse Function From a Table. Authored by: Mathispower4u. License: All Rights Reserved. License terms: Standard YouTube License.
- College Algebra. Provided by: OpenStax Authored by: Abramson, Jay et al.. Located at: https://openstax.org/books/college-algebra/pages/1-introduction-to-prerequisites. License: CC BY: Attribution. License terms: Download for free at http://cnx.org/contents/[email protected].
