Algebraic Operations with Radical Expressions
Learning Objectives
- Multiply and divide radical expressions
- Use the product raised to a power rule to multiply radical expressions
- Use the quotient raised to a power rule to divide radical expressions
- Add and subtract radical expressions
- Determine when two radicals have the same index and radicand
- Recognize when a radical expression can be simplified either before or after addition or subtraction
- Multiply multiple term radicals
- Use the distributive property to multiply multiple term radicals
- Use the power of a product rule to simplify products of multiple term radicals
- Rationalize a denominator containing a radical expression
- Define and recognize a rational number
- Rationalize denominators with one or multiple terms
Multiply and Divide Radical Expressions
You can do more than just simplify radical expressions. You can multiply and divide them, too. The product raised to a power rule that we discussed previously will help us find products of radical expressions. Recall the rule:A Product Raised to a Power Rule
For any numbers a and b and any integer x: [latex] {{(ab)}^{x}}={{a}^{x}}\cdot {{b}^{x}}[/latex] For any numbers a and b and any positive integer x: [latex]\displaystyle {{(ab)}^{\frac{1}{x}}}={{a}^{\frac{1}{x}}}\cdot {{b}^{\frac{1}{x}}}[/latex] For any numbers a and b and any positive integer x: [latex] \sqrt[x]{ab}=\sqrt[x]{a}\cdot \sqrt[x]{b}[/latex]Example
Simplify. [latex] \sqrt{18}\cdot \sqrt{16}[/latex]Answer: Use the rule [latex] \sqrt[x]{a}\cdot \sqrt[x]{b}=\sqrt[x]{ab}[/latex] to multiply the radicands.
[latex]\begin{array}{r}\sqrt{18\cdot 16}\\\sqrt{288}\end{array}[/latex]
Look for perfect squares in the radicand, and rewrite the radicand as the product of two factors.[latex] \sqrt{144\cdot 2}[/latex]
Identify perfect squares.[latex] \sqrt{{{(12)}^{2}}\cdot 2}[/latex]
Rewrite as the product of two radicals.[latex] \sqrt{{{(12)}^{2}}}\cdot \sqrt{2}[/latex]
Simplify, using [latex] \sqrt{{{x}^{2}}}=\left| x \right|[/latex].[latex]\begin{array}{r}\left| 12 \right|\cdot \sqrt{2}\\12\cdot \sqrt{2}\end{array}[/latex]
Answer
[latex-display] \sqrt{18}\cdot \sqrt{16}=12\sqrt{2}[/latex-display]Example
Simplify. [latex] \sqrt{18}\cdot \sqrt{16}[/latex]Answer: Look for perfect squares in each radicand, and rewrite as the product of two factors.
[latex] \begin{array}{r}\sqrt{9\cdot 2}\cdot \sqrt{4\cdot 4}\\\sqrt{3\cdot 3\cdot 2}\cdot \sqrt{4\cdot 4}\end{array}[/latex]
Identify perfect squares.[latex] \sqrt{{{(3)}^{2}}\cdot 2}\cdot \sqrt{{{(4)}^{2}}}[/latex]
Rewrite as the product of radicals.[latex] \sqrt{{{(3)}^{2}}}\cdot \sqrt{2}\cdot \sqrt{{{(4)}^{2}}}[/latex]
Simplify, using [latex] \sqrt{{{x}^{2}}}=\left| x \right|[/latex].[latex]\begin{array}{c}\left|3\right|\cdot\sqrt{2}\cdot\left|4\right|\\3\cdot\sqrt{2}\cdot4\end{array}[/latex]
Multiply.[latex] 12[/latex]
Answer
[latex-display] \sqrt{18}\cdot \sqrt{16}=12\sqrt{2}[/latex-display]Example
Simplify. [latex] \sqrt{12{{x}^{4}}}\cdot \sqrt{3x^2}[/latex], [latex] x\ge 0[/latex]Answer: Use the rule [latex] \sqrt[x]{a}\cdot \sqrt[x]{b}=\sqrt[x]{ab}[/latex] to multiply the radicands.
[latex] \sqrt{12{{x}^{4}}\cdot 3x^2}\\\sqrt{12\cdot 3\cdot {{x}^{4}}\cdot x^2}[/latex]
Recall that [latex] {{x}^{4}}\cdot x^2={{x}^{4+2}}[/latex].[latex]\begin{array}{r}\sqrt{36\cdot {{x}^{4+2}}}\\\sqrt{36\cdot {{x}^{6}}}\end{array}[/latex]
Look for perfect squares in the radicand.[latex] \sqrt{{{(6)}^{2}}\cdot {{({{x}^{3}})}^{2}}}[/latex]
Rewrite as the product of radicals.[latex] \begin{array}{c}\sqrt{{{(6)}^{2}}}\cdot \sqrt{{{({{x}^{3}})}^{2}}}\\6\cdot {{x}^{3}}\end{array}[/latex]
Answer
[latex-display] \sqrt{12{{x}^{4}}}\cdot \sqrt{3x^2}=6{{x}^{3}}[/latex-display]Analysis of the solution
Even though our answer contained a variable with an odd exponent that was simplified from an even indexed root, we don't need to write our answer with absolute value because we specified before we simplified that [latex] x\ge 0[/latex]. It is important to read the problem very well when you are doing math. Even the smallest statement like [latex] x\ge 0[/latex] can influence the way you write your answer. In our next example we will multiply two cube roots.Example
Simplify. [latex] \sqrt[3]{{{x}^{5}}{{y}^{2}}}\cdot 5\sqrt[3]{8{{x}^{2}}{{y}^{4}}}[/latex]Answer: Notice that both radicals are cube roots, so you can use the rule [latex] [/latex] to multiply the radicands.
[latex]\begin{array}{l}5\sqrt[3]{{{x}^{5}}{{y}^{2}}\cdot 8{{x}^{2}}{{y}^{4}}}\\5\sqrt[3]{8\cdot {{x}^{5}}\cdot {{x}^{2}}\cdot {{y}^{2}}\cdot {{y}^{4}}}\\5\sqrt[3]{8\cdot {{x}^{5+2}}\cdot {{y}^{2+4}}}\\5\sqrt[3]{8\cdot {{x}^{7}}\cdot {{y}^{6}}}\end{array}[/latex]
Look for perfect cubes in the radicand. Since [latex] {{x}^{7}}[/latex] is not a perfect cube, it has to be rewritten as [latex] {{x}^{6+1}}={{({{x}^{2}})}^{3}}\cdot x[/latex].[latex] 5\sqrt[3]{{{(2)}^{3}}\cdot {{({{x}^{2}})}^{3}}\cdot x\cdot {{({{y}^{2}})}^{3}}}[/latex]
Rewrite as the product of radicals.[latex] \begin{array}{r}5\sqrt[3]{{{(2)}^{3}}}\cdot \sqrt[3]{{{({{x}^{2}})}^{3}}}\cdot \sqrt[3]{{{({{y}^{2}})}^{3}}}\cdot \sqrt[3]{x}\\5\cdot 2\cdot {{x}^{2}}\cdot {{y}^{2}}\cdot \sqrt[3]{x}\end{array}[/latex]
Answer
[latex-display] \sqrt[3]{{{x}^{5}}{{y}^{2}}}\cdot 5\sqrt[3]{8{{x}^{2}}{{y}^{4}}}=10{{x}^{2}}{{y}^{2}}\sqrt[3]{x}[/latex-display]Example
Simplify. [latex] 2\sqrt[4]{16{{x}^{9}}}\cdot \sqrt[4]{{{y}^{3}}}\cdot \sqrt[4]{81{{x}^{3}}y}[/latex], [latex] x\ge 0[/latex], [latex] y\ge 0[/latex]Answer: Notice this expression is multiplying three radicals with the same (fourth) root. Simplify each radical, if possible, before multiplying. Be looking for powers of 4 in each radicand.
[latex] 2\sqrt[4]{{{(2)}^{4}}\cdot {{({{x}^{2}})}^{4}}\cdot x}\cdot \sqrt[4]{{{y}^{3}}}\cdot \sqrt[4]{{{(3)}^{4}}\cdot {{x}^{3}}y}[/latex]
Rewrite as the product of radicals.[latex] 2\sqrt[4]{{{(2)}^{4}}}\cdot \sqrt[4]{{{({{x}^{2}})}^{4}}}\cdot \sqrt[4]{x}\cdot \sqrt[4]{{{y}^{3}}}\cdot \sqrt[4]{{{(3)}^{4}}}\cdot \sqrt[4]{{{x}^{3}}y}[/latex]
Identify and pull out powers of 4, using the fact that [latex] \sqrt[4]{{{x}^{4}}}=\left| x \right|[/latex].[latex] \begin{array}{r}2\cdot \left| 2 \right|\cdot \left| {{x}^{2}} \right|\cdot \sqrt[4]{x}\cdot \sqrt[4]{{{y}^{3}}}\cdot \left| 3 \right|\cdot \sqrt[4]{{{x}^{3}}y}\\2\cdot 2\cdot {{x}^{2}}\cdot \sqrt[4]{x}\cdot \sqrt[4]{{{y}^{3}}}\cdot 3\cdot \sqrt[4]{{{x}^{3}}y}\end{array}[/latex]
Since all the radicals are fourth roots, you can use the rule [latex] \sqrt[x]{ab}=\sqrt[x]{a}\cdot \sqrt[x]{b}[/latex] to multiply the radicands.[latex]\begin{array}{r}2\cdot 2\cdot 3\cdot {{x}^{2}}\cdot \sqrt[4]{x\cdot {{y}^{3}}\cdot {{x}^{3}}y}\\12{{x}^{2}}\sqrt[4]{{{x}^{1+3}}\cdot {{y}^{3+1}}}\end{array}[/latex]
Now that the radicands have been multiplied, look again for powers of 4, and pull them out. We can drop the absolute value signs in our final answer because at the start of the problem we were told [latex] x\ge 0[/latex], [latex] y\ge 0[/latex].[latex] \begin{array}{l}12{{x}^{2}}\sqrt[4]{{{x}^{4}}\cdot {{y}^{4}}}\\12{{x}^{2}}\sqrt[4]{{{x}^{4}}}\cdot \sqrt[4]{{{y}^{4}}}\\12{{x}^{2}}\cdot \left| x \right|\cdot \left| y \right|\end{array}[/latex]
Answer
[latex-display] 2\sqrt[4]{16{{x}^{9}}}\cdot \sqrt[4]{{{y}^{3}}}\cdot \sqrt[4]{81{{x}^{3}}y}=12{{x}^{3}}y,\,\,x\ge 0,\,\,y\ge 0[/latex-display]Dividing Radical Expressions
You can use the same ideas to help you figure out how to simplify and divide radical expressions. Recall that the Product Raised to a Power Rule states that [latex] \sqrt[x]{ab}=\sqrt[x]{a}\cdot \sqrt[x]{b}[/latex]. Well, what if you are dealing with a quotient instead of a product? There is a rule for that, too. The Quotient Raised to a Power Rule states that [latex]\displaystyle {{\left( \frac{a}{b} \right)}^{x}}=\frac{{{a}^{x}}}{{{b}^{x}}}[/latex]. Again, if you imagine that the exponent is a rational number, then you can make this rule applicable for roots as well: [latex]\displaystyle {{\left( \frac{a}{b} \right)}^{\frac{1}{x}}}=\frac{{{a}^{\frac{1}{x}}}}{{{b}^{\frac{1}{x}}}}[/latex], so [latex]\displaystyle \sqrt[x]{\frac{a}{b}}=\frac{\sqrt[x]{a}}{\sqrt[x]{b}}[/latex].A Quotient Raised to a Power Rule
For any real numbers a and b (b ≠ 0) and any positive integer x: [latex]\displaystyle {{\left( \frac{a}{b} \right)}^{\frac{1}{x}}}=\frac{{{a}^{\frac{1}{x}}}}{{{b}^{\frac{1}{x}}}}[/latex] For any real numbers a and b (b ≠ 0) and any positive integer x: [latex]\displaystyle \sqrt[x]{\frac{a}{b}}=\frac{\sqrt[x]{a}}{\sqrt[x]{b}}[/latex]Example
Simplify. [latex]\displaystyle \sqrt{\frac{48}{25}}[/latex]Answer: Use the rule [latex]\displaystyle \sqrt[x]{\frac{a}{b}}=\frac{\sqrt[x]{a}}{\sqrt[x]{b}}[/latex] to create two radicals; one in the numerator and one in the denominator.
[latex]\displaystyle \frac{\sqrt{48}}{\sqrt{25}}[/latex]
Simplify each radical. Look for perfect square factors in the radicand, and rewrite the radicand as a product of factors.[latex]\displaystyle \begin{array}{c}\frac{\sqrt{16\cdot 3}}{\sqrt{25}}\\\\\text{or}\\\\\frac{\sqrt{4\cdot 4\cdot 3}}{\sqrt{5\cdot 5}}\end{array}[/latex]
Identify and pull out perfect squares.[latex]\displaystyle \begin{array}{r}\frac{\sqrt{{{(4)}^{2}}\cdot 3}}{\sqrt{{{(5)}^{2}}}}\\\\\frac{\sqrt{{{(4)}^{2}}}\cdot \sqrt{3}}{\sqrt{{{(5)}^{2}}}}\end{array}[/latex]
Simplify.[latex]\displaystyle \frac{4\cdot \sqrt{3}}{5}[/latex]
Answer
[latex-display]\displaystyle \sqrt{\frac{48}{25}}=\frac{4\sqrt{3}}{5}[/latex-display]Example
Simplify. [latex]\displaystyle \sqrt[3]{\frac{640}{40}}[/latex]Answer: Rewrite using the Quotient Raised to a Power Rule.
[latex]\displaystyle \frac{\sqrt[3]{640}}{\sqrt[3]{40}}[/latex]
Simplify each radical. Look for perfect cubes in the radicand, and rewrite the radicand as a product of factors.[latex]\displaystyle \frac{\sqrt[3]{64\cdot 10}}{\sqrt[3]{8\cdot 5}}[/latex]
Identify and pull out perfect cubes.[latex]\displaystyle \begin{array}{r}\frac{\sqrt[3]{{{(4)}^{3}}\cdot 10}}{\sqrt[3]{{{(2)}^{3}}\cdot 5}}\\\\\frac{\sqrt[3]{{{(4)}^{3}}}\cdot \sqrt[3]{10}}{\sqrt[3]{{{(2)}^{3}}}\cdot \sqrt[3]{5}}\\\\\frac{4\cdot \sqrt[3]{10}}{2\cdot \sqrt[3]{5}}\end{array}[/latex]
You can simplify this expression even further by looking for common factors in the numerator and denominator.[latex]\displaystyle \frac{4\sqrt[3]{10}}{2\sqrt[3]{5}}[/latex]
Rewrite the numerator as a product of factors.[latex]\displaystyle \frac{2\cdot 2\sqrt[3]{5}\cdot \sqrt[3]{2}}{2\sqrt[3]{5}}[/latex]
Identify factors of 1, and simplify.[latex]\displaystyle \begin{array}{r}2\cdot \frac{2\sqrt[3]{5}}{2\sqrt[3]{5}}\cdot \sqrt[3]{2}\\\\2\cdot 1\cdot \sqrt[3]{2}\end{array}[/latex]
Answer
[latex-display]\displaystyle \sqrt[3]{\frac{640}{40}}=2\sqrt[3]{2}[/latex-display]Example
Simplify. [latex]\displaystyle \frac{\sqrt[3]{640}}{\sqrt[3]{40}}[/latex]Answer: Since both radicals are cube roots, you can use the rule [latex]\displaystyle \frac{\sqrt[x]{a}}{\sqrt[x]{b}}=\sqrt[x]{\frac{a}{b}}[/latex] to create a single rational expression underneath the radical.
[latex]\displaystyle \sqrt[3]{\frac{640}{40}}[/latex]
Within the radical, divide 640 by 40.[latex] \begin{array}{r}640\div 40=16\\\sqrt[3]{16}\end{array}[/latex]
Look for perfect cubes in the radicand, and rewrite the radicand as a product of factors.[latex]\sqrt[3]{8\cdot2}[/latex]
Identify perfect cubes and pull them out.[latex] \begin{array}{r}\sqrt[3]{{{(2)}^{3}}\cdot 2}\\\sqrt[3]{2}\end{array}[/latex]
Simplify.[latex]2\cdot\sqrt[3]{2}[/latex]
Answer
[latex-display]\displaystyle\frac{\sqrt[3]{640}}{\sqrt[3]{40}}=2\sqrt[3]{2}[/latex-display]Example
Simplify. [latex]\displaystyle \frac{\sqrt{30x}}{\sqrt{10x}},x>0[/latex]Answer: Use the Quotient Raised to a Power Rule to rewrite this expression.
[latex]\displaystyle \sqrt{\frac{30x}{10x}}[/latex]
Simplify [latex]\displaystyle \sqrt{\frac{30x}{10x}}[/latex] by identifying similar factors in the numerator and denominator and then identifying factors of 1.[latex]\displaystyle \begin{array}{r}\sqrt{\frac{3\cdot10x}{10x}}\\\\\sqrt{3\cdot\frac{10x}{10x}}\\\\\sqrt{3\cdot1}\end{array}[/latex]
Answer
[latex-display]\displaystyle \frac{\sqrt{30x}}{\sqrt{10x}}=\sqrt{3}[/latex-display]Example
Simplify. [latex]\displaystyle \frac{\sqrt[3]{24x{{y}^{4}}}}{\sqrt[3]{8y}},\,\,y\ne 0[/latex]Answer: Use the Quotient Raised to a Power Rule to rewrite this expression.
[latex]\displaystyle \sqrt[3]{\frac{24x{{y}^{4}}}{8y}}[/latex]
Simplify [latex]\displaystyle \sqrt[3]{\frac{24x{{y}^{4}}}{8y}}[/latex] by identifying similar factors in the numerator and denominator and then identifying factors of 1.[latex]\displaystyle \begin{array}{l}\sqrt[3]{\frac{8\cdot 3\cdot x\cdot {{y}^{3}}\cdot y}{8\cdot y}}\\\\\sqrt[3]{\frac{3\cdot x\cdot {{y}^{3}}}{1}\cdot \frac{8y}{8y}}\\\\\sqrt[3]{\frac{3\cdot x\cdot {{y}^{3}}}{1}\cdot 1}\end{array}[/latex]
Identify perfect cubes and pull them out of the radical.[latex] \sqrt[3]{3x{{y}^{3}}}\\\sqrt[3]{{{(y)}^{3}}\cdot \,3x}[/latex]
Simplify.[latex] \sqrt[3]{{{(y)}^{3}}}\cdot \,\sqrt[3]{3x}[/latex]
Answer
[latex-display] \frac{\sqrt[3]{24x{{y}^{4}}}}{\sqrt[3]{8y}}=y\,\sqrt[3]{3x}[/latex-display]Add and Subtract Radical Expressions
There are two keys to combining radicals by addition or subtraction: look at the index, and look at the radicand. If these are the same, then addition and subtraction are possible. If not, then you cannot combine the two radicals. In the graphic below, the index of the expression [latex]12\sqrt[3]{xy}[/latex] is 3 and the radicand is [latex]xy[/latex].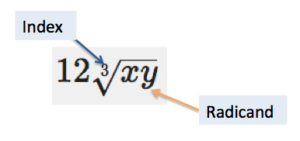 Making sense of a string of radicals may be difficult. One helpful tip is to think of radicals as variables, and treat them the same way. When you add and subtract variables, you look for like terms, which is the same thing you will do when you add and subtract radicals.
In this first example, both radicals have the same radicand and index.
Making sense of a string of radicals may be difficult. One helpful tip is to think of radicals as variables, and treat them the same way. When you add and subtract variables, you look for like terms, which is the same thing you will do when you add and subtract radicals.
In this first example, both radicals have the same radicand and index.
Example
Add. [latex] 3\sqrt{11}+7\sqrt{11}[/latex]Answer: The two radicals are the same, [latex] [/latex]. This means you can combine them as you would combine the terms [latex] 3a+7a[/latex].
[latex] \text{3}\sqrt{11}\text{ + 7}\sqrt{11}[/latex]
Answer
[latex-display] 3\sqrt{11}+7\sqrt{11}=10\sqrt{11}[/latex-display]Example
Add. [latex] 5\sqrt{2}+\sqrt{3}+4\sqrt{3}+2\sqrt{2}[/latex]Answer: Rearrange terms so that like radicals are next to each other. Then add.
[latex] 5\sqrt{2}+2\sqrt{2}+\sqrt{3}+4\sqrt{3}[/latex]
Answer
[latex-display] 5\sqrt{2}+\sqrt{3}+4\sqrt{3}+2\sqrt{2}=7\sqrt{2}+5\sqrt{3}[/latex-display]Example
Add. [latex] 3\sqrt{x}+12\sqrt[3]{xy}+\sqrt{x}[/latex]Answer: Rearrange terms so that like radicals are next to each other. Then add.
[latex] 3\sqrt{x}+\sqrt{x}+12\sqrt[3]{xy}[/latex]
Answer
[latex-display] 3\sqrt{x}+12\sqrt[3]{xy}+\sqrt{x}=4\sqrt{x}+12\sqrt[3]{xy}[/latex-display]Example
Add and simplify. [latex] 2\sqrt[3]{40}+\sqrt[3]{135}[/latex]Answer: Simplify each radical by identifying perfect cubes.
[latex] \begin{array}{r}2\sqrt[3]{8\cdot 5}+\sqrt[3]{27\cdot 5}\\2\sqrt[3]{{{(2)}^{3}}\cdot 5}+\sqrt[3]{{{(3)}^{3}}\cdot 5}\\2\sqrt[3]{{{(2)}^{3}}}\cdot \sqrt[3]{5}+\sqrt[3]{{{(3)}^{3}}}\cdot \sqrt[3]{5}\end{array}[/latex]
Simplify.[latex] 2\cdot 2\cdot \sqrt[3]{5}+3\cdot \sqrt[3]{5}[/latex]
Add.[latex]4\sqrt[3]{5}+3\sqrt[3]{5}[/latex]
Answer
[latex-display] 2\sqrt[3]{40}+\sqrt[3]{135}=7\sqrt[3]{5}[/latex-display]Example
Add and simplify. [latex] x\sqrt[3]{x{{y}^{4}}}+y\sqrt[3]{{{x}^{4}}y}[/latex]Answer: Simplify each radical by identifying perfect cubes.
[latex]\begin{array}{r}x\sqrt[3]{x\cdot {{y}^{3}}\cdot y}+y\sqrt[3]{{{x}^{3}}\cdot x\cdot y}\\x\sqrt[3]{{{y}^{3}}}\cdot \sqrt[3]{xy}+y\sqrt[3]{{{x}^{3}}}\cdot \sqrt[3]{xy}\\xy\cdot \sqrt[3]{xy}+xy\cdot \sqrt[3]{xy}\end{array}[/latex]
Add like radicals.[latex] xy\sqrt[3]{xy}+xy\sqrt[3]{xy}[/latex]
Answer
[latex-display] x\sqrt[3]{x{{y}^{4}}}+y\sqrt[3]{{{x}^{4}}y}=2xy\sqrt[3]{xy}[/latex-display]Subtract Radicals
Subtraction of radicals follows the same set of rules and approaches as addition—the radicands and the indices must be the same for two (or more) radicals to be subtracted. In the three examples that follow, subtraction has been rewritten as addition of the opposite.Example
Subtract. [latex] 5\sqrt{13}-3\sqrt{13}[/latex]Answer: The radicands and indices are the same, so these two radicals can be combined.
[latex] 5\sqrt{13}-3\sqrt{13}[/latex]
Answer
[latex-display] 5\sqrt{13}-3\sqrt{13}=2\sqrt{13}[/latex-display]Example
Subtract. [latex] 4\sqrt[3]{5a}-\sqrt[3]{3a}-2\sqrt[3]{5a}[/latex]Answer: Two of the radicals have the same index and radicand, so they can be combined. Rewrite the expression so that like radicals are next to each other.
[latex] 4\sqrt[3]{5a}+(-\sqrt[3]{3a})+(-2\sqrt[3]{5a})\\4\sqrt[3]{5a}+(-2\sqrt[3]{5a})+(-\sqrt[3]{3a})[/latex]
Combine. Although the indices of [latex] 2\sqrt[3]{5a}[/latex] and [latex] -\sqrt[3]{3a}[/latex] are the same, the radicands are not—so they cannot be combined.[latex] 2\sqrt[3]{5a}+(-\sqrt[3]{3a})[/latex]
Answer
[latex-display] 4\sqrt[3]{5a}-\sqrt[3]{3a}-2\sqrt[3]{5a}=2\sqrt[3]{5a}-\sqrt[3]{3a}[/latex-display] In the following video we show more examples of subtracting radical expressions when no simplifying is required. https://youtu.be/77TR9HsPZ6MExample
Subtract and simplify. [latex] 5\sqrt[4]{{{a}^{5}}b}-a\sqrt[4]{16ab}[/latex], where [latex]a\ge 0[/latex] and [latex]b\ge 0[/latex]Answer: Simplify each radical by identifying and pulling out powers of 4.
[latex]\begin{array}{r}5\sqrt[4]{{{a}^{4}}\cdot a\cdot b}-a\sqrt[4]{{{(2)}^{4}}\cdot a\cdot b}\\5\cdot a\sqrt[4]{a\cdot b}-a\cdot 2\sqrt[4]{a\cdot b}\\5a\sqrt[4]{ab}-2a\sqrt[4]{ab}\end{array}[/latex]
Answer
[latex-display] 5\sqrt[4]{{{a}^{5}}b}-a\sqrt[4]{16ab}=3a\sqrt[4]{ab}[/latex-display]Multiple Term Radicals
When multiplying multiple term radical expressions it is important to follow the Distributive Property of Multiplication, as when you are multiplying regular, non-radical expressions. Radicals follow the same mathematical rules that other real numbers do. So, although the expression [latex] \sqrt{x}(3\sqrt{x}-5)[/latex] may look different than [latex] a(3a-5)[/latex], you can treat them the same way. Let’s have a look at how to apply the Distributive Property. First let’s do a problem with the variable a, and then solve the same problem replacing a with [latex] \sqrt{x}[/latex].Example
Simplify. [latex] a(3a-5)[/latex]Answer: Use the Distributive Property of Multiplication over Subtraction.
[latex]\begin{array}{c}a(3a)-a(5)\\=3a^2-5a\end{array}[/latex]
Answer
[latex-display] a(3a-5)=3{{a}^{2}}-5a[/latex-display]Example
Simplify. [latex] \sqrt{x}(3\sqrt{x}-5)[/latex]Answer: Use the Distributive Property of Multiplication over Subtraction.
[latex] \sqrt{x}(3\sqrt{x})-\sqrt{x}(5)[/latex]
Apply the rules of multiplying radicals: [latex] \sqrt{a}\cdot \sqrt{b}=\sqrt{ab}[/latex] to multiply [latex] \sqrt{x}(3\sqrt{x})[/latex].[latex] 3\sqrt{{{x}^{2}}}-5\sqrt{x}[/latex]
Be sure to simplify radicals when you can: [latex] \sqrt{{{x}^{2}}}=\left| x \right|[/latex], so [latex] 3\sqrt{{{x}^{2}}}=3\left| x \right|[/latex].Answer
[latex-display] \sqrt{x}(3\sqrt{x}-5)=3\left| x \right|-5\sqrt{x}[/latex-display]Example
Simplify. [latex] 7\sqrt{x}\left( 2\sqrt{xy}+\sqrt{y} \right)[/latex]Answer: Use the Distributive Property of Multiplication over Addition to multiply each term within parentheses by [latex] 7\sqrt{x}[/latex].
[latex] 7\sqrt{x}\left( 2\sqrt{xy} \right)+7\sqrt{x}\left( \sqrt{y} \right)[/latex]
Apply the rules of multiplying radicals.[latex] 7\cdot 2\sqrt{{{x}^{2}}y}+7\sqrt{xy}[/latex]
[latex] \sqrt{{{x}^{2}}}=\left| x \right|[/latex], so [latex] \left| x \right|[/latex] can be pulled out of the radical.[latex] 14|x|\sqrt{y}+7\sqrt{xy}[/latex]
Answer
[latex-display] 7\sqrt{x}\left( 2\sqrt{xy}+\sqrt{y} \right)=14\left| x \right|\sqrt{y}+7\sqrt{xy}[/latex-display]Example
Simplify. [latex] \sqrt[3]{a}\left( 2\sqrt[3]{{{a}^{2}}}-4\sqrt[3]{{{a}^{5}}}+8\sqrt[3]{{{a}^{8}}} \right)[/latex]Answer: Use the Distributive Property.
[latex] \sqrt[3]{a}\left( 2\sqrt[3]{{{a}^{2}}} \right)-\sqrt[3]{a}\left( 4\sqrt[3]{{{a}^{5}}} \right)+\sqrt[3]{a}\left( 8\sqrt[3]{{{a}^{8}}} \right)[/latex]
Apply the rules of multiplying radicals.[latex] \begin{array}{c}2\sqrt[3]{a\cdot {{a}^{2}}}-4\sqrt[3]{a\cdot {{a}^{5}}}+8\sqrt[3]{a\cdot {{a}^{8}}}\\2\sqrt[3]{{{a}^{3}}}-4\sqrt[3]{{{a}^{6}}}+8\sqrt[3]{{{a}^{9}}}\end{array}[/latex]
Identify cubes in each of the radicals.[latex] 2\sqrt[3]{{{a}^{3}}}-4\sqrt[3]{{{\left( {{a}^{2}} \right)}^{3}}}+8\sqrt[3]{{{\left( {{a}^{3}} \right)}^{3}}}[/latex]
Answer
[latex-display] \sqrt[3]{a}\left( 2\sqrt[3]{{{a}^{2}}}-4\sqrt[3]{{{a}^{5}}}+8\sqrt[3]{{{a}^{8}}} \right)=2a-4{{a}^{2}}+8{{a}^{3}}[/latex-display]Multiply Binomial Expressions That Contain Radicals
You can use the same technique for multiplying binomials to multiply binomial expressions with radicals. As a refresher, here is the process for multiplying two binomials. If you like using the expression “FOIL” (First, Outside, Inside, Last) to help you figure out the order in which the terms should be multiplied, you can use it here, too.Example
Multiply. [latex] \left( 2x+5 \right)\left( 3x-2 \right)[/latex]Answer: Use the Distributive Property.
[latex]\begin{array}{l}\text{First}:\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,2x\cdot 3x=6{{x}^{2}}\\\text{Outside}:\,\,\,2x\cdot \left( -2 \right)=-4x\\\text{Inside}:\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,5\cdot 3x=15x\\\text{Last}:\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,5\cdot \left( -2 \right)=-10\end{array}[/latex]
Record the terms, and then combine like terms.[latex] 6{{x}^{2}}-4x+15x-10[/latex]
Answer
[latex-display] \left( 2x+5 \right)\left( 3x-2 \right)=6{{x}^{2}}+11x-10[/latex-display]Example
Multiply. [latex] \left( 2\sqrt{b}+5 \right)\left( 3\sqrt{b}-2 \right),\,\,b\ge 0[/latex]Answer: Use the Distributive Property to multiply. Simplify using [latex] \sqrt{x}\cdot \sqrt{x}=x[/latex].
[latex]\begin{array}{l}\text{First}:\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,2\sqrt{b}\cdot 3\sqrt{b}=2\cdot 3\cdot \sqrt{b}\cdot \sqrt{b}=6b\\\text{Outside}:\,\,\,2\sqrt{b}\cdot \left( -2 \right)=-4\sqrt{b}\\\text{Inside}:\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,5\cdot 3\sqrt{b}=15\sqrt{b}\\\text{Last}:\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,5\cdot \left( -2 \right)=-10\end{array}[/latex]
Record the terms, and then combine like terms.[latex] 6b-4\sqrt{b}+15\sqrt{b}-10[/latex]
Answer
[latex-display] \left( 2\sqrt{b}+5 \right)\left( 3\sqrt{b}-2 \right)=6b+11\sqrt{b}-10[/latex-display]Multiplying Two-Term Radical Expressions
To multiply radical expressions, use the same method as used to multiply polynomials.- Use the Distributive Property (or, if you prefer, the shortcut FOIL method);
- Remember that [latex] \sqrt{a}\cdot \sqrt{b}=\sqrt{ab}[/latex]; and
- Combine like terms.
Example
Multiply. [latex] \left( 4{{x}^{2}}+\sqrt[3]{x} \right)\left( \sqrt[3]{{{x}^{2}}}+2 \right)[/latex]Answer: Use FOIL to multiply.
[latex]\begin{array}{l}\text{First}:\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,4x^{2}\cdot\sqrt[3]{x^{2}}=4x^{2}\sqrt[3]{x^{2}}\\\text{Outside}:\,\,\,4x^{2}\cdot 2=8x^{2}\\\text{Inside}:\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\sqrt[3]{x}\cdot\sqrt[3]{x^{2}}=\sqrt[3]{x^{2}\cdot x}=\sqrt[3]{x^{3}}=x\\\text{Last}:\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\,\sqrt[3]{x}\cdot 2=2\sqrt[3]{x}\end{array}[/latex]
Record the terms, and then combine like terms (if possible). Here, there are no like terms to combine.[latex] 4{{x}^{2}}\sqrt[3]{{{x}^{2}}}+8{{x}^{2}}+x+2\sqrt[3]{x}[/latex]
Answer
[latex-display] \left( 4{{x}^{2}}+\sqrt[3]{x} \right)\left( \sqrt[3]{{{x}^{2}}}+2 \right)=4{{x}^{2}}\sqrt[3]{{{x}^{2}}}+8{{x}^{2}}+x+2\sqrt[3]{x}[/latex-display]Rationalize Denominators
Although radicals follow the same rules that integers do, it is often difficult to figure out the value of an expression containing radicals. For example, you probably have a good sense of how much [latex]\displaystyle \frac{4}{8},\ 0.75[/latex] and [latex]\displaystyle \frac{6}{9}[/latex] are, but what about the quantities [latex]\displaystyle \frac{1}{\sqrt{2}}[/latex] and [latex]\displaystyle \frac{1}{\sqrt{5}}[/latex]? These are much harder to visualize. That said, sometimes you have to work with expressions that contain many radicals. Often the value of these expressions is not immediately clear. In cases where you have a fraction with a radical in the denominator, you can use a technique called rationalizing a denominator to eliminate the radical. The point of rationalizing a denominator is to make it easier to understand what the quantity really is by removing radicals from the denominators. The idea of rationalizing a denominator makes a bit more sense if you consider the definition of “rationalize.” Recall that the numbers 5, [latex]\displaystyle \frac{1}{2}[/latex], and [latex] 0.75[/latex] are all known as rational numbers—they can each be expressed as a ratio of two integers ([latex]\displaystyle \frac{5}{1},\frac{1}{2}[/latex], and [latex]\displaystyle \frac{3}{4}[/latex] respectively). Some radicals are irrational numbers because they cannot be represented as a ratio of two integers. As a result, the point of rationalizing a denominator is to change the expression so that the denominator becomes a rational number. Here are some examples of irrational and rational denominators.|
Irrational |
Rational |
|
|---|---|---|
|
[latex]\displaystyle \frac{1}{\sqrt{2}}[/latex] |
= |
[latex]\displaystyle \frac{\sqrt{2}}{2}[/latex] |
|
[latex]\displaystyle \frac{2+\sqrt{3}}{\sqrt{3}}[/latex] |
= |
[latex]\displaystyle \frac{2\sqrt{3}+3}{3}[/latex] |
Rationalizing Denominators with One Term
Let’s start with the fraction [latex]\displaystyle \frac{1}{\sqrt{2}}[/latex]. Its denominator is [latex] \sqrt{2}[/latex], an irrational number. This makes it difficult to figure out what the value of [latex]\displaystyle \frac{1}{\sqrt{2}}[/latex] is. You can rename this fraction without changing its value, if you multiply it by 1. In this case, set 1 equal to [latex]\displaystyle \frac{\sqrt{2}}{\sqrt{2}}[/latex]. Watch what happens.[latex]\displaystyle \frac{1}{\sqrt{2}}\cdot 1=\frac{1}{\sqrt{2}}\cdot \frac{\sqrt{2}}{\sqrt{2}}=\frac{\sqrt{2}}{\sqrt{2\cdot 2}}=\frac{\sqrt{2}}{\sqrt{4}}=\frac{\sqrt{2}}{2}[/latex]
The denominator of the new fraction is no longer a radical (notice, however, that the numerator is). So why choose to multiply [latex]\displaystyle \frac{1}{\sqrt{2}}[/latex] by [latex]\displaystyle \frac{\sqrt{2}}{\sqrt{2}}[/latex]? You knew that the square root of a number times itself will be a whole number. In algebraic terms, this idea is represented by [latex] \sqrt{x}\cdot \sqrt{x}=x[/latex]. Look back to the denominators in the multiplication of [latex]\displaystyle \frac{1}{\sqrt{2}}\cdot 1[/latex]. Do you see where [latex] \sqrt{2}\cdot \sqrt{2}=\sqrt{4}=2[/latex]? In the following videos we show examples of rationalizing the denominator of a radical expression that contains integer radicands. https://youtu.be/K7NdhPLVl7g Here are some more examples. Notice how the value of the fraction is not changed at all—it is simply being multiplied by another name for 1.Example
Rationalize the denominator.[latex]\displaystyle \frac{2+\sqrt{3}}{\sqrt{3}}[/latex]
Answer: The denominator of this fraction is [latex] \sqrt{3}[/latex]. To make it into a rational number, multiply it by [latex] \sqrt{3}[/latex], since [latex] \sqrt{3}\cdot \sqrt{3}=3[/latex].
[latex]\displaystyle \frac{2+\sqrt{3}}{\sqrt{3}}[/latex]
Multiply the entire fraction by another name for 1, [latex]\displaystyle \frac{\sqrt{3}}{\sqrt{3}}[/latex].[latex]\displaystyle\begin{array}{r}\frac{2+\sqrt{3}}{\sqrt{3}}\cdot \frac{\sqrt{3}}{\sqrt{3}}\\\\\frac{\sqrt{3}(2+\sqrt{3})}{\sqrt{3}\cdot \sqrt{3}}\end{array}[/latex]
Use the Distributive Property to multiply [latex] \sqrt{3}(2+\sqrt{3})[/latex].[latex]\displaystyle \frac{2\sqrt{3}+\sqrt{3}\cdot \sqrt{3}}{\sqrt{9}}[/latex]
Simplify the radicals, where possible. [latex] \sqrt{9}=3[/latex].[latex]\displaystyle \frac{2\sqrt{3}+\sqrt{9}}{\sqrt{9}}[/latex]
Answer
[latex-display]\displaystyle \frac{2+\sqrt{3}}{\sqrt{3}}=\frac{2\sqrt{3}+3}{3}[/latex-display]Example
Rationalize the denominator.[latex]\displaystyle \frac{\sqrt{x}+\sqrt{y}}{\sqrt{x}},\text{ where }x\ne \text{0}[/latex]
Answer: The denominator is [latex] \sqrt{x}[/latex], so the entire expression can be multiplied by [latex]\displaystyle \frac{\sqrt{x}}{\sqrt{x}}[/latex] to get rid of the radical in the denominator.
[latex]\displaystyle \begin{array}{c}\frac{\sqrt{x}+\sqrt{y}}{\sqrt{x}}\cdot \frac{\sqrt{x}}{\sqrt{x}}\\\\\frac{\sqrt{x}(\sqrt{x}+\sqrt{y})}{\sqrt{x}\cdot \sqrt{x}}\end{array}[/latex]
Use the Distributive Property. Simplify the radicals, where possible. Remember that [latex] \sqrt{x}\cdot \sqrt{x}=x[/latex].[latex]\displaystyle \frac{\sqrt{x}\cdot \sqrt{x}+\sqrt{x}\cdot \sqrt{y}}{\sqrt{x}\cdot \sqrt{x}}[/latex]
Answer
[latex-display]\displaystyle \frac{\sqrt{x}+\sqrt{y}}{\sqrt{x}}=\frac{x+\sqrt{xy}}{x}[/latex-display]Example
Rationalize the denominator and simplify.[latex]\displaystyle \sqrt{\frac{100x}{11y}},\text{ where }y\ne \text{0}[/latex]
Answer: Rewrite [latex]\displaystyle \sqrt{\frac{a}{b}}[/latex] as [latex]\displaystyle \frac{\sqrt{a}}{\sqrt{b}}[/latex].
[latex]\displaystyle \frac{\sqrt{100x}}{\sqrt{11y}}[/latex]
The denominator is [latex] \sqrt{11y}[/latex], so multiplying the entire expression by [latex]\displaystyle \frac{\sqrt{11y}}{\sqrt{11y}}[/latex] will rationalize the denominator.[latex]\displaystyle \frac{\sqrt{100x\cdot11y}}{\sqrt{11y}\cdot\sqrt{11y}}[/latex]
Multiply and simplify the radicals, where possible.[latex]\displaystyle \frac{\sqrt{100\cdot 11xy}}{\sqrt{11y}\cdot \sqrt{11y}}[/latex]
100 is a perfect square. Remember that[latex] \sqrt{100}=10[/latex] and [latex] \sqrt{x}\cdot \sqrt{x}=x[/latex].[latex]\displaystyle \frac{\sqrt{100}\cdot \sqrt{11xy}}{\sqrt{11y}\cdot \sqrt{11y}}[/latex]
Answer
[latex-display]\displaystyle \sqrt{\frac{100x}{11y}}=\frac{10\sqrt{11xy}}{11y}[/latex-display]Rationalizing the denominator with higher roots
When we rationalized a square root, we multiplied the numerator and denominator by a square root that would give us a perfect square under the radical in the denominator. When we took the square root, the denominator no longer had a radical.
We will follow a similar process to rationalize higher roots. To rationalize a denominator with a higher index radical, we multiply the numerator and denominator by a radical that would give us a radicand that is a perfect power of the index. When we simplify the new radical, the denominator will no longer have a radical.
For example,
ExAMPLE
Rationalize the denominator and simplify. [latex]\displaystyle \frac{1}{\sqrt[3]{6}}[/latex]Answer: The radical in the denominator has one factor of 6. We multiply both the numerator and the denominator by [latex]\sqrt[3]{6^2}[/latex], which gives us 2 more factors of 6.
[latex]\displaystyle \frac{1 \cdot (\sqrt[3]{6^2})}{\sqrt[3]{6} \cdot (\sqrt[3]{6^2})}[/latex]
Multiply. Notice the radicand in the denominator has 3 powers of 6.[latex]\displaystyle \frac{\sqrt[3]{6^2}}{\sqrt[3]{6^3}}[/latex]
Finally, simplify the cube root in the denominator.[latex]\displaystyle \frac{\sqrt[3]{36}}{6}[/latex]
Answer [latex-display]\displaystyle \frac{\sqrt[3]{36}}{6}[/latex-display]ExAMPLE
Rationalize the denominator and simplify. [latex]\displaystyle \frac{3}{\sqrt[3]{4x}}[/latex]Answer: Rewrite the radicand to show the factors.
[latex]\displaystyle \frac{3}{\sqrt[3]{2^2 \cdot x}}[/latex]
Multiply the numerator and denominator by [latex]\sqrt[3]{2 \cdot x^2}[/latex]. This will get us 3 factors of 2 and 3 factors of [latex]x[/latex].[latex]\displaystyle \frac{3 \cdot (\sqrt[3]{2 \cdot x^2})}{\sqrt[3]{2^2 \cdot x} \cdot (\sqrt[3]{2 \cdot x^2})}[/latex]
Simplify.[latex]\displaystyle \frac{3\sqrt[3]{2x^2}}{\sqrt[3]{2^3x^3}}[/latex]
Simplify the radical in the denominator.[latex]\displaystyle \frac{3\sqrt[3]{2x^2}}{2x}[/latex]
Answer [latex-display]\displaystyle \frac{3\sqrt[3]{2x^2}}{2x}[/latex-display]Try It
[ohm_question]19018[/ohm_question]Rationalizing Denominators with Two Terms
Denominators do not always contain just one term, as shown in the previous examples. Sometimes, you will see expressions like [latex]\displaystyle \frac{3}{\sqrt{2}+3}[/latex] where the denominator is composed of two terms, [latex] \sqrt{2}[/latex] and [latex]+3[/latex]. Unfortunately, you cannot rationalize these denominators the same way you rationalize single-term denominators. If you multiply [latex] \sqrt{2}+3[/latex] by [latex] \sqrt{2}[/latex], you get [latex] 2+3\sqrt{2}[/latex]. The original [latex] \sqrt{2}[/latex] is gone, but now the quantity [latex] 3\sqrt{2}[/latex] has appeared...this is no better! In order to rationalize this denominator, you want to square the radical term and somehow prevent the integer term from being multiplied by a radical. Is this possible? It is possible—and you have already seen how to do it! Recall that when binomials of the form [latex] (a+b)(a-b)[/latex] are multiplied, the product is [latex] [/latex]. So, for example, [latex] (x+3)(x-3)={{x}^{2}}-3x+3x-9={{x}^{2}}-9[/latex]; notice that the terms [latex]−3x[/latex] and [latex]+3x[/latex] combine to 0. Now for the connection to rationalizing denominators: what if you replaced x with [latex] \sqrt{2}[/latex]? Look at the side by side examples below. Just as [latex] -3x+3x[/latex] combines to 0 on the left, [latex] -3\sqrt{2}+3\sqrt{2}[/latex] combines to 0 on the right.| [latex] \begin{array}{l}(x+3)(x-3)\\={{x}^{2}}-3x+3x-9\\={{x}^{2}}-9\end{array}[/latex] | [latex] \begin{array}{l}\left( \sqrt{2}+3 \right)\left( \sqrt{2}-3 \right)\\={{\left( \sqrt{2} \right)}^{2}}-3\sqrt{2}+3\sqrt{2}-9\\={{\left( \sqrt{2} \right)}^{2}}-9\\=2-9\\=-7\end{array}[/latex] |
| Term | Conjugate | Product |
|---|---|---|
| [latex] \sqrt{2}+3[/latex] | [latex] \sqrt{2}-3[/latex] | [latex] \left( \sqrt{2}+3 \right)\left( \sqrt{2}-3 \right)={{\left( \sqrt{2} \right)}^{2}}-{{\left( 3 \right)}^{2}}=2-9=-7[/latex] |
| [latex] \sqrt{x}-5[/latex] | [latex] \sqrt{x}+5[/latex] | [latex] \left( \sqrt{x}-5 \right)\left( \sqrt{x}+5 \right)={{\left( \sqrt{x} \right)}^{2}}-{{\left( 5 \right)}^{2}}=x-25[/latex] |
| [latex] 8-2\sqrt{x}[/latex] | [latex] 8+2\sqrt{x}[/latex] | [latex] \left( 8-2\sqrt{x} \right)\left( 8+2\sqrt{x} \right)={{\left( 8 \right)}^{2}}-{{\left( 2\sqrt{x} \right)}^{2}}=64-4x[/latex] |
| [latex] 1+\sqrt{xy}[/latex] | [latex] 1-\sqrt{xy}[/latex] | [latex] \left( 1+\sqrt{xy} \right)\left( 1-\sqrt{xy} \right)={{\left( 1 \right)}^{2}}-{{\left( \sqrt{xy} \right)}^{2}}=1-xy[/latex] |
Example
Rationalize the denominator and simplify.[latex]\displaystyle \frac{5-\sqrt{7}}{3+\sqrt{5}}[/latex]
Answer: Find the conjugate of [latex] 3+\sqrt{5}[/latex]. Then multiply the entire expression by [latex]\displaystyle \frac{3-\sqrt{5}}{3-\sqrt{5}}[/latex].
[latex]\displaystyle \begin{array}{c}\frac{5-\sqrt{7}}{3+\sqrt{5}}\cdot \frac{3-\sqrt{5}}{3-\sqrt{5}}\\\\\frac{\left( 5-\sqrt{7} \right)\left( 3-\sqrt{5} \right)}{\left( 3+\sqrt{5} \right)\left( 3-\sqrt{5} \right)}\end{array}[/latex]
Use the Distributive Property to multiply the binomials in the numerator and denominator.[latex]\displaystyle \frac{5\cdot 3-5\sqrt{5}-3\sqrt{7}+\sqrt{7}\cdot \sqrt{5}}{3\cdot 3-3\sqrt{5}+3\sqrt{5}-\sqrt{5}\cdot \sqrt{5}}[/latex]
Since you multiplied by the conjugate of the denominator, the radical terms in the denominator will combine to 0.[latex]\displaystyle \frac{15-5\sqrt{5}-3\sqrt{7}+\sqrt{35}}{9-3\sqrt{5}+3\sqrt{5}-\sqrt{25}}[/latex]
Simplify radicals where possible.[latex]\displaystyle \begin{array}{c}\frac{15-5\sqrt{5}-3\sqrt{7}+\sqrt{35}}{9-\sqrt{25}}\\\\\frac{15-5\sqrt{5}-3\sqrt{7}+\sqrt{35}}{9-5}\end{array}[/latex]
Answer
[latex-display]\displaystyle \frac{5-\sqrt{7}}{3+\sqrt{5}}=\frac{15-5\sqrt{5}-3\sqrt{7}+\sqrt{35}}{4}[/latex-display]Example
Rationalize the denominator and simplify.[latex]\displaystyle \frac{\sqrt{x}}{\sqrt{x}+2}[/latex]
Answer: Find the conjugate of [latex] \sqrt{x}+2[/latex]. Then multiply the numerator and denominator by [latex]\displaystyle \frac{\sqrt{x}-2}{\sqrt{x}-2}[/latex].
[latex]\displaystyle \begin{array}{c}\frac{\sqrt{x}}{\sqrt{x}+2}\cdot \frac{\sqrt{x}-2}{\sqrt{x}-2}\\\\\frac{\sqrt{x}\left( \sqrt{x}-2 \right)}{\left( \sqrt{x}+2 \right)\left( \sqrt{x}-2 \right)}\end{array}[/latex]
Use the Distributive Property to multiply the binomials in the numerator and denominator.[latex]\displaystyle \frac{\sqrt{x}\cdot \sqrt{x}-2\sqrt{x}}{\sqrt{x}\cdot \sqrt{x}-2\sqrt{x}+2\sqrt{x}-2\cdot 2}[/latex]
Simplify. Remember that [latex] \sqrt{x}\cdot \sqrt{x}=x[/latex]. Since you multiplied by the conjugate of the denominator, the radical terms in the denominator will combine to 0.[latex]\displaystyle \frac{\sqrt{x}\cdot \sqrt{x}-2\sqrt{x}}{\sqrt{x}\cdot \sqrt{x}-2\sqrt{x}+2\sqrt{x}-4}[/latex]
Answer
[latex-display]\displaystyle \frac{\sqrt{x}}{\sqrt{x}+2}=\frac{x-2\sqrt{x}}{x-4}[/latex-display][latex] \begin{array}{l}\left( \sqrt[3]{10}+5 \right)\left( \sqrt[3]{10}-5 \right)\\={{\left( \sqrt[3]{10} \right)}^{2}}-5\sqrt[3]{10}+5\sqrt[3]{10}-25\\={{\left( \sqrt[3]{10} \right)}^{2}}-25\\=\sqrt[3]{100}-25\end{array}[/latex]
[latex] \sqrt[3]{100}[/latex] cannot be simplified any further, since its prime factors are [latex] 2\cdot 2\cdot 5\cdot 5[/latex]. There are no cubed numbers to pull out! Multiplying [latex] \sqrt[3]{10}+5[/latex] by its conjugate does not result in a radical-free expression. In the following video we show more examples of how to rationalize a denominator using the conjugate. https://youtu.be/vINRIRgeKqULicenses & Attributions
CC licensed content, Original
- Multiply Square Roots. Authored by: James Sousa (Mathispower4u.com) for Lumen Learning. License: CC BY: Attribution.
- Multiply Cube Roots. Authored by: James Sousa (Mathispower4u.com) for Lumen Learning. License: CC BY: Attribution.
- Dividing Radicals without Variables (Basic with no rationalizing). Authored by: James Sousa (Mathispower4u.com) for Lumen Learning. License: CC BY: Attribution.
- Dividing Radicals with Variables (Basic with no rationalizing). Authored by: James Sousa (Mathispower4u.com) for Lumen Learning. License: CC BY: Attribution.
- Revision and Adaptation. Provided by: Lumen Learning License: CC BY: Attribution.
- Adding Radicals (Basic With No Simplifying). Authored by: James Sousa (Mathispower4u.com) for Lumen Learning. License: CC BY: Attribution.
- Adding Radicals That Requires Simplifying. Authored by: James Sousa (Mathispower4u.com) for Lumen Learning. License: CC BY: Attribution.
- Subtracting Radicals (Basic With No Simplifying). Authored by: James Sousa (Mathispower4u.com) for Lumen Learning. License: CC BY: Attribution.
- Subtracting Radicals That Requires Simplifying. Authored by: James Sousa (Mathispower4u.com) for Lumen Learning. License: Public Domain: No Known Copyright.
- Multiplying Radical Expressions with Variables Using Distribution. Authored by: James Sousa (Mathispower4u.com) for Lumen Learning. License: CC BY: Attribution.
- Multiplying Binomial Radical Expressions with Variables. Authored by: James Sousa (Mathispower4u.com) for Lumen Learning. License: CC BY: Attribution.
CC licensed content, Shared previously
- Unit 16: Radical Expressions and Quadratic Equations, from Developmental Math: An Open Program. Provided by: Monterey Institute of Technology Located at: https://www.nroc.org/. License: CC BY: Attribution.
- Precalculus. Provided by: OpenStax Authored by: Abramson, Jay. Located at: https://cnx.org/contents/[email protected]:1/Preface. License: CC BY: Attribution. License terms: Dwonload fro free at : http://cnx.org/contents/[email protected]:1/Preface.
- Ex 1: Rationalize the Denominator of a Radical Expression. Authored by: James Sousa (Mathispower4u.com) . License: CC BY: Attribution.
- Ex: Rationalize the Denominator of a Radical Expression - Conjugate. Authored by: James Sousa (Mathispower4u.com) . License: CC BY: Attribution.
- Intermediate Algebra. Authored by: Lynn Marecek. Located at: https://openstax.org/books/intermediate-algebra/pages/1-introduction. License: CC BY: Attribution. License terms: Download for free at http://cnx.org/contents/[email protected].
- Question ID#19018. Authored by: Wallace,Tyler, mb Lippman,David. License: CC BY: Attribution.

