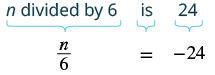Example
Translate and solve: [latex]n[/latex] divided by [latex]6[/latex] is [latex]-24[/latex].
Solution:
| Translate. |
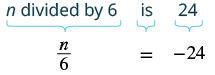 |
| Multiply both sides by [latex]6[/latex] . |
[latex]\color{red}{6}\cdot\frac{n}{6}=\color{red}{6}(-24)[/latex] |
| Simplify. |
[latex]n=-144[/latex] |
| Check: |
Is [latex]-144[/latex] divided by [latex]6[/latex] equal to [latex]-24[/latex] ? |
|
| Translate. |
[latex]\frac{-144}{6}\stackrel{?}{=}-24[/latex] |
|
| Simplify. It checks. |
[latex]-24=-24[/latex] |
|
Example
Translate and solve: The quotient of [latex]q[/latex] and [latex]-5[/latex] is [latex]70[/latex].
Answer:
Solution:
| Translate. |
 |
| Multiply both sides by [latex]-5[/latex] . |
[latex]\color{red}{5}(\frac{q}{-5}) = \color{red}{-5}(70)[/latex] |
| Simplify. |
[latex]q=-350[/latex] |
| Check: |
Is the quotient of [latex]-350[/latex] and [latex]-5[/latex] equal to [latex]70[/latex] ? |
|
| Translate. |
[latex]\frac{-350}{-5}\stackrel{?}{=}70[/latex] |
|
| Simplify. It checks. |
[latex]70=70[/latex] |
|
Example
Translate and solve: Two-thirds of [latex]f[/latex] is [latex]18[/latex].
Answer:
Solution:
| Translate. |
 |
| Multiply both sides by [latex]\frac{3}{2}[/latex] . |
[latex]\color{red}{\frac{3}{2}}\cdot\frac{2}{3}f=\color{red}{\frac{3}{2}}\cdot 18[/latex] |
| Simplify. |
[latex]f=27[/latex] |
| Check: |
Is two-thirds of [latex]27[/latex] equal to [latex]18[/latex] ? |
|
| Translate. |
[latex]\frac{2}{3}(27)\stackrel{?}{=}18[/latex] |
|
| Simplify. It checks. |
[latex]18=18[/latex] |
|
Example
Translate and solve: The quotient of [latex]m[/latex] and [latex]\frac{5}{6}[/latex] is [latex]\frac{3}{4}[/latex].
Answer:
Solution:
|
The quotient of [latex]m[/latex] and [latex]\frac{5}{6}[/latex] is [latex]\frac{3}{4}[/latex] . |
| Translate. |
[latex]\frac{m}{\frac{5}{6}}=\frac{3}{4}[/latex] |
| Multiply both sides by [latex]\frac{5}{6}[/latex] to isolate [latex]m[/latex] . |
[latex]\frac{5}{6}\left(\frac{m}{\frac{5}{6}}\right)=\frac{5}{6}\left(\frac{3}{4}\right)[/latex] |
| Simplify. |
[latex]m=\frac{5\cdot 3}{6\cdot 4}[/latex] |
| Remove common factors and multiply. |
[latex]m=\frac{5}{8}[/latex] |
| Check: |
|
|
| Is the quotient of [latex]\frac{5}{8}[/latex] and [latex]\frac{5}{6}[/latex] equal to [latex]\frac{3}{4}[/latex] ? |
[latex]\frac{\frac{5}{8}}{\frac{5}{6}}\stackrel{?}{=}\frac{3}{4}[/latex] |
|
| Rewrite as division. |
[latex]\frac{5}{8}\div \frac{5}{6}\stackrel{?}{=}\frac{3}{4}[/latex] |
|
| Multiply the first fraction by the reciprocal of the second. |
[latex]\frac{5}{8}\cdot \frac{6}{5}\stackrel{?}{=}\frac{3}{4}[/latex] |
|
| Simplify. |
[latex]\frac{3}{4}=\frac{3}{4}[/latex] |
|
Our solution checks.
Example
Translate and solve: The sum of three-eighths and [latex]x[/latex] is three and one-half.
Answer:
Solution:
| Translate. |
 |
| Use the Subtraction Property of Equality to subtract [latex]\frac{3}{8}[/latex] from both sides. |
[latex]\frac{3}{8}+x-\frac{3}{8}=3\frac{1}{2}-\frac{3}{8}[/latex] |
| Combine like terms on the left side. |
[latex]x=3\frac{1}{2}-\frac{3}{8}[/latex] |
| Convert mixed number to improper fraction. |
[latex]x\frac{7}{2}-\frac{3}{8}[/latex] |
| Convert to equivalent fractions with LCD of [latex]8[/latex]. |
[latex]x=\frac{28}{8}-\frac{3}{8}[/latex] |
| Subtract. |
[latex]x=\frac{25}{8}[/latex] |
| Write as a mixed number. |
[latex]x=3\frac{1}{8}[/latex] |
We write the answer as a mixed number because the original problem used a mixed number.
Check:
Is the sum of three-eighths and [latex]3\frac{1}{8}[/latex] equal to three and one-half?
|
[latex]\frac{3}{8}+3\frac{1}{8}\stackrel{?}{=}3\frac{1}{2}[/latex] |
| Add. |
[latex]3\frac{4}{8}\stackrel{?}{=}3\frac{1}{2}[/latex] |
| Simplify. |
[latex]3\frac{1}{2}=3\frac{1}{2}[/latex] |
The solution checks.