Solutions
Solutions to Try Its
1. The sequence is arithmetic. The common difference is [latex]-2[/latex]. 2. The sequence is not arithmetic because [latex]3 - 1\ne 6 - 3[/latex]. 3. [latex]\left\{1, 6, 11, 16, 21\right\}[/latex] 4. [latex]{a}_{2}=2[/latex] 5. [latex]\begin{array}{l}{a}_{1}=25\hfill \\ {a}_{n}={a}_{n - 1}+12,\text{ for }n\ge 2\hfill \end{array}[/latex] 6. [latex]{a}_{n}=53 - 3n[/latex] 7. There are 11 terms in the sequence. 8. The formula is [latex]{T}_{n}=10+4n[/latex], and it will take her 42 minutes.Solutions to Odd-Numbered Exercises
1. A sequence where each successive term of the sequence increases (or decreases) by a constant value. 3. We find whether the difference between all consecutive terms is the same. This is the same as saying that the sequence has a common difference. 5. Both arithmetic sequences and linear functions have a constant rate of change. They are different because their domains are not the same; linear functions are defined for all real numbers, and arithmetic sequences are defined for natural numbers or a subset of the natural numbers. 7. The common difference is [latex]\frac{1}{2}[/latex] 9. The sequence is not arithmetic because [latex]16 - 4\ne 64 - 16[/latex]. 11. [latex]0,\frac{2}{3},\frac{4}{3},2,\frac{8}{3}[/latex] 13. [latex]0,-5,-10,-15,-20[/latex] 15. [latex]{a}_{4}=19[/latex] 17. [latex]{a}_{6}=41[/latex] 19. [latex]{a}_{1}=2[/latex] 21. [latex]{a}_{1}=5[/latex] 23. [latex]{a}_{1}=6[/latex] 25. [latex]{a}_{21}=-13.5[/latex] 27. [latex]-19,-20.4,-21.8,-23.2,-24.6[/latex] 29. [latex]\begin{array}{ll}{a}_{1}=17; {a}_{n}={a}_{n - 1}+9\hfill & n\ge 2\hfill \end{array}[/latex] 31. [latex]\begin{array}{ll}{a}_{1}=12; {a}_{n}={a}_{n - 1}+5\hfill & n\ge 2\hfill \end{array}[/latex] 33. [latex]\begin{array}{ll}{a}_{1}=8.9; {a}_{n}={a}_{n - 1}+1.4\hfill & n\ge 2\hfill \end{array}[/latex] 35. [latex]\begin{array}{ll}{a}_{1}=\frac{1}{5}; {a}_{n}={a}_{n - 1}+\frac{1}{4}\hfill & n\ge 2\hfill \end{array}[/latex] 37. [latex]\begin{array}{ll}{}_{1}=\frac{1}{6}; {a}_{n}={a}_{n - 1}-\frac{13}{12}\hfill & n\ge 2\hfill \end{array}[/latex] 39. [latex]{a}_{1}=4;\text{ }{a}_{n}={a}_{n - 1}+7;\text{ }{a}_{14}=95[/latex] 41. First five terms: [latex]20,16,12,8,4[/latex]. 43. [latex]{a}_{n}=1+2n[/latex] 45. [latex]{a}_{n}=-105+100n[/latex] 47. [latex]{a}_{n}=1.8n[/latex] 49. [latex]{a}_{n}=13.1+2.7n[/latex] 51. [latex]{a}_{n}=\frac{1}{3}n-\frac{1}{3}[/latex] 53. There are 10 terms in the sequence. 55. There are 6 terms in the sequence. 57. The graph does not represent an arithmetic sequence. 59.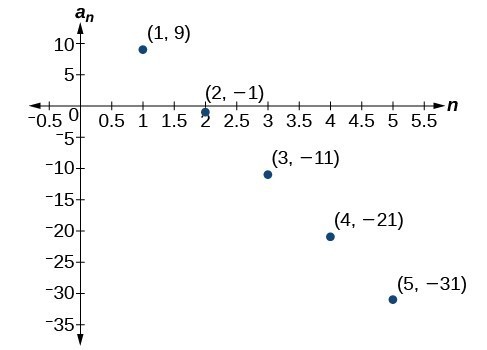 61. [latex]1,4,7,10,13,16,19[/latex]
63.
61. [latex]1,4,7,10,13,16,19[/latex]
63.
 65.
65.
 67. Answers will vary. Examples: [latex]{a}_{n}=20.6n[/latex] and [latex]{a}_{n}=2+20.4\mathrm{n.}[/latex]
69. [latex]{a}_{11}=-17a+38b[/latex]
71. The sequence begins to have negative values at the 13th term, [latex]{a}_{13}=-\frac{1}{3}[/latex]
73. Answers will vary. Check to see that the sequence is arithmetic. Example: Recursive formula: [latex]{a}_{1}=3,{a}_{n}={a}_{n - 1}-3[/latex]. First 4 terms: [latex]\begin{array}{ll}3,0,-3,-6\hfill & {a}_{31}=-87\hfill \end{array}[/latex]
67. Answers will vary. Examples: [latex]{a}_{n}=20.6n[/latex] and [latex]{a}_{n}=2+20.4\mathrm{n.}[/latex]
69. [latex]{a}_{11}=-17a+38b[/latex]
71. The sequence begins to have negative values at the 13th term, [latex]{a}_{13}=-\frac{1}{3}[/latex]
73. Answers will vary. Check to see that the sequence is arithmetic. Example: Recursive formula: [latex]{a}_{1}=3,{a}_{n}={a}_{n - 1}-3[/latex]. First 4 terms: [latex]\begin{array}{ll}3,0,-3,-6\hfill & {a}_{31}=-87\hfill \end{array}[/latex]Licenses & Attributions
CC licensed content, Specific attribution
- Precalculus. Provided by: OpenStax Authored by: OpenStax College. Located at: https://cnx.org/contents/[email protected]:1/Preface. License: CC BY: Attribution.
