Read: Define Logarithmic Functions
Learning Objectives
- Define a logarithmic function as the inverse of an exponential function
- Convert between logarithmic and exponential forms
In order to analyze the magnitude of earthquakes or compare the magnitudes of two different earthquakes, we need to be able to convert between logarithmic and exponential form. For example, suppose the amount of energy released from one earthquake were [latex]500[/latex] times greater than the amount of energy released from another. We want to calculate the difference in magnitude. The equation that represents this problem is [latex]{10}^{x}=500[/latex], where x represents the difference in magnitudes on the Richter Scale. How would we solve for x?
We have not yet learned a method for solving exponential equations. None of the algebraic tools discussed so far is sufficient to solve [latex]{10}^{x}=500[/latex]. We know that [latex]{10}^{2}=100[/latex] and [latex]{10}^{3}=1000[/latex], so it is clear that x must be some value between [latex]2[/latex] and [latex]3[/latex], since [latex]y={10}^{x}[/latex] is increasing. We can examine a graph to better estimate the solution.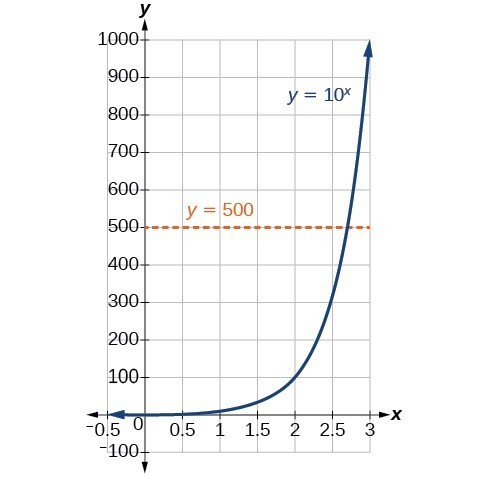 Figure 2
Figure 2Estimating from a graph, however, is imprecise. To find an algebraic solution, we must introduce a new function. Observe that the graph above passes the horizontal line test. The exponential function [latex]y={b}^{x}[/latex] is one-to-one, so its inverse, [latex]x={b}^{y}[/latex] is also a function. As is the case with all inverse functions, we simply interchange x and y and solve for y to find the inverse function. To represent y as a function of x, we use a logarithmic function of the form [latex]y={\mathrm{log}}_{b}\left(x\right)[/latex]. The base b logarithm of a number is the exponent by which we must raise b to get that number.
We read a logarithmic expression as, "The logarithm with base b of x is equal to y," or, simplified, "log base b of x is y." We can also say, "b raised to the power of y is x," because logs are exponents. For example, the base [latex]2[/latex] logarithm of [latex]32[/latex] is [latex]5[/latex], because [latex]5[/latex] is the exponent we must apply to [latex]2[/latex] to get [latex]32[/latex]. Since [latex]{2}^{5}=32[/latex], we can write [latex]{\mathrm{log}}_{2}32=5[/latex]. We read this as "log base [latex]2[/latex] of [latex]32[/latex] is [latex]5[/latex]."
We can express the relationship between logarithmic form and its corresponding exponential form as follows:
Note that the base b is always positive.

Because logarithm is a function, it is most correctly written as [latex]{\mathrm{log}}_{b}\left(x\right)[/latex], using parentheses to denote function evaluation, just as we would with [latex]f\left(x\right)[/latex]. However, when the input is a single variable or number, it is common to see the parentheses dropped and the expression written without parentheses, as [latex]{\mathrm{log}}_{b}x[/latex]. Note that many calculators require parentheses around the x.
We can illustrate the notation of logarithms as follows:

Notice that, comparing the logarithm function and the exponential function, the input and the output are switched. This means [latex]y={\mathrm{log}}_{b}\left(x\right)[/latex] and [latex]y={b}^{x}[/latex] are inverse functions.
Definition of the Logarithmic Function
A logarithm base b of a positive number x satisfies the following definition.
For [latex]x>0,b>0,b\ne 1[/latex],
where,
- we read [latex]{\mathrm{log}}_{b}\left(x\right)[/latex] as, "the logarithm with base b of x" or the "log base b of x."
- the logarithm y is the exponent to which b must be raised to get x.
Also, since the logarithmic and exponential functions switch the x and y values, the domain and range of the exponential function are interchanged for the logarithmic function. Therefore,
- the domain of the logarithm function with base [latex]b \text{ is} \left(0,\infty \right)[/latex].
- the range of the logarithm function with base [latex]b \text{ is} \left(-\infty ,\infty \right)[/latex].
Example
Write the following logarithmic equations in exponential form.
- [latex]{\mathrm{log}}_{6}\left(\sqrt{6}\right)=\frac{1}{2}[/latex]
- [latex]{\mathrm{log}}_{3}\left(9\right)=2[/latex]
Answer:
First, identify the values of b, y, and x. Then, write the equation in the form [latex]{b}^{y}=x[/latex].
- [latex]{\mathrm{log}}_{6}\left(\sqrt{6}\right)=\frac{1}{2}[/latex]
Here, [latex]b=6,y=\frac{1}{2},\text{and } x=\sqrt{6}[/latex]. Therefore, the equation [latex]{\mathrm{log}}_{6}\left(\sqrt{6}\right)=\frac{1}{2}[/latex] is equivalent to [latex]{6}^{\frac{1}{2}}=\sqrt{6}[/latex].
- [latex]{\mathrm{log}}_{3}\left(9\right)=2[/latex]
Here, b =[latex]3[/latex], y =[latex]2[/latex], and x =[latex]9[/latex]. Therefore, the equation [latex]{\mathrm{log}}_{3}\left(9\right)=2[/latex] is equivalent to [latex]{3}^{2}=9[/latex].
- [latex]{\mathrm{log}}_{6}\left(\sqrt{6}\right)=\frac{1}{2}[/latex]
How To: Given an equation in logarithmic form [latex]{\mathrm{log}}_{b}\left(x\right)=y[/latex], convert it to exponential form.
- Examine the equation [latex]y={\mathrm{log}}_{b}x[/latex] and identify b, y, and x.
- Rewrite [latex]{\mathrm{log}}_{b}x=y[/latex] as [latex]{b}^{y}=x[/latex].
Think About It
Can we take the logarithm of a negative number? Re-read the definition of a logarithm and formulate an answer. Think about the behavior of exponents. You can use the textbox below to formulate your ideas before you look at an answer.
[practice-area rows="1"][/practice-area]Answer:
No. Because the base of an exponential function is always positive, no power of that base can ever be negative. We can never take the logarithm of a negative number. Also, we cannot take the logarithm of zero. Calculators may output a log of a negative number when in complex mode, but the log of a negative number is not a real number.
Convert from exponential to logarithmic form
To convert from exponents to logarithms, we follow the same steps in reverse. We identify the base b, exponent x, and output y. Then we write [latex]x={\mathrm{log}}_{b}\left(y\right)[/latex].Example
Write the following exponential equations in logarithmic form.
- [latex]{2}^{3}=8[/latex]
- [latex]{5}^{2}=25[/latex]
- [latex]{10}^{-4}=\frac{1}{10,000}[/latex]
Answer:
First, identify the values of b, y, and x. Then, write the equation in the form [latex]x={\mathrm{log}}_{b}\left(y\right)[/latex].
- [latex]{2}^{3}=8[/latex]
Here, b =[latex]2, <em>x </em>= 3[/latex], and [latex]<em>y </em>= 8[/latex]. Therefore, the equation [latex]{2}^{3}=8[/latex] is equivalent to [latex]{\mathrm{log}}_{2}\left(8\right)=3[/latex].
- [latex]{5}^{2}=25[/latex]
Here, [latex]<em>b </em>= 5[/latex],[latex]<em>x </em>= 2[/latex], and [latex]<em>y </em>= 25[/latex]. Therefore, the equation [latex]{5}^{2}=25[/latex] is equivalent to [latex]{\mathrm{log}}_{5}\left(25\right)=2[/latex].
- [latex]{10}^{-4}=\frac{1}{10,000}[/latex]
Here,[latex]<em>b </em>= 10[/latex],[latex]<em>x </em>= –4[/latex], and [latex]y=\frac{1}{10,000}[/latex]. Therefore, the equation [latex]{10}^{-4}=\frac{1}{10,000}[/latex] is equivalent to [latex]{\text{log}}_{10}\left(\frac{1}{10,000}\right)=-4[/latex].
- [latex]{2}^{3}=8[/latex]
Summary
The base b logarithm of a number is the exponent by which we must raise b to get that number. Logarithmic functions are the inverse of Exponential functions, and it is often easier to understand them through this lens. We can never take the logarithm of a negative number, therefore [latex]{\mathrm{log}}_{b}\left(x\right)=y[/latex] is defined for [latex]b>0[/latex]Licenses & Attributions
CC licensed content, Original
- Ex: Write Exponential Equations as Logarithmic Equations. Authored by: James Sousa (Mathispower4u.com) for Lumen Learning. License: CC BY: Attribution.
- Revision and Adaptation. Provided by: Lumen Learning License: CC BY: Attribution.
CC licensed content, Shared previously
- Precalculus. Provided by: OpenStax Authored by: Jay Abramson, et al.. Located at: https://openstax.org/books/precalculus/pages/1-introduction-to-functions. License: CC BY: Attribution. License terms: Download For Free at : http://cnx.org/contents/[email protected]..
- Ex: Write Logarithmic Equations as Exponential Equations. Authored by: James Sousa (Mathispower4u.com) for Lumen Learning. License: CC BY: Attribution.
