Presenting Categorical Data Graphically
Learning Outcomes
- Create a frequency table, bar graph, pareto chart, pictogram, or a pie chart to represent a data set
- Identify features of ineffective representations of data
- Create a histogram, pie chart, or frequency polygon that represents numerical data
- Create a graph that compares two quantities
Visualizing Data
Categorical, or qualitative, data are pieces of information that allow us to classify the objects under investigation into various categories. We usually begin working with categorical data by summarizing the data into a frequency table.Frequency Table
A frequency table is a table with two columns. One column lists the categories, and another for the frequencies with which the items in the categories occur (how many items fit into each category).Example
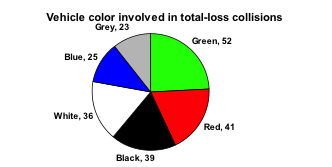
An insurance company determines vehicle insurance premiums based on known risk factors. If a person is considered a higher risk, their premiums will be higher. One potential factor is the color of your car. The insurance company believes that people with some color cars are more likely to get in accidents. To research this, they examine police reports for recent total-loss collisions. The data is summarized in the frequency table below.| Color | Frequency |
| Blue | 25 |
| Green | 52 |
| Red | 41 |
| White | 36 |
| Black | 39 |
| Grey | 23 |
Bar graph
A bar graph is a graph that displays a bar for each category with the length of each bar indicating the frequency of that category.example
Using our car data from above, note the highest frequency is 52, so our vertical axis needs to go from 0 to 52, but we might as well use 0 to 55, so that we can put a hash mark every 5 units: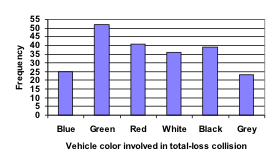 Notice that the height of each bar is determined by the frequency of the corresponding color. The horizontal gridlines are a nice touch, but not necessary. In practice, you will find it useful to draw bar graphs using graph paper, so the gridlines will already be in place, or using technology. Instead of gridlines, we might also list the frequencies at the top of each bar, like this:
Notice that the height of each bar is determined by the frequency of the corresponding color. The horizontal gridlines are a nice touch, but not necessary. In practice, you will find it useful to draw bar graphs using graph paper, so the gridlines will already be in place, or using technology. Instead of gridlines, we might also list the frequencies at the top of each bar, like this:
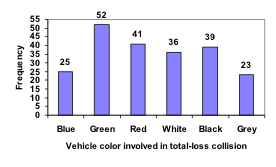 The following video explains the process and value of moving data from a table to a bar graph.
https://youtu.be/vwxKf_O3ui0
The following video explains the process and value of moving data from a table to a bar graph.
https://youtu.be/vwxKf_O3ui0
Pareto chart
A Pareto chart is a bar graph ordered from highest to lowest frequencyExamples
Transforming our bar graph from earlier into a Pareto chart, we get: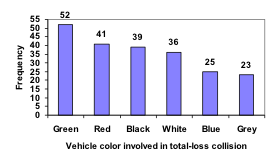 The following video addressed Pareto charts.
https://youtu.be/Tsvru8DPxBE
The following video addressed Pareto charts.
https://youtu.be/Tsvru8DPxBE
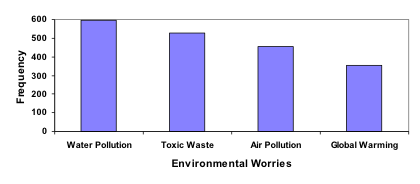
In a survey[footnote]Gallup Poll. March 5-8, 2009. http://www.pollingreport.com/enviro.htm[/footnote], adults were asked whether they personally worried about a variety of environmental concerns. The numbers (out of 1012 surveyed) who indicated that they worried “a great deal” about some selected concerns are summarized below.
| Environmental Issue | Frequency |
| Pollution of drinking water | 597 |
| Contamination of soil and water by toxic waste | 526 |
| Air pollution | 455 |
| Global warming | 354 |
Pie Chart
A pie chart is a circle with wedges cut of varying sizes marked out like slices of pie or pizza. The relative sizes of the wedges correspond to the relative frequencies of the categories.examples
For our vehicle color data, a pie chart might look like this: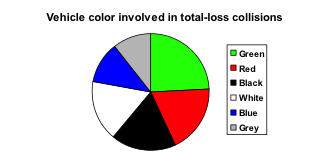 Pie charts can often benefit from including frequencies or relative frequencies (percents) in the chart next to the pie slices. Often having the category names next to the pie slices also makes the chart clearer.
Pie charts can often benefit from including frequencies or relative frequencies (percents) in the chart next to the pie slices. Often having the category names next to the pie slices also makes the chart clearer.
 This video demonstrates how to create pie charts like the ones above.
https://youtu.be/__1f8dKh6yo
This video demonstrates how to create pie charts like the ones above.
https://youtu.be/__1f8dKh6yo
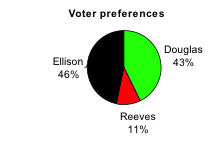
The pie chart below shows the percentage of voters supporting each candidate running for a local senate seat. If there are 20,000 voters in the district, the pie chart shows that about 11% of those, about 2,200 voters, support Reeves.
 The following video addresses how to read a pie chart like the one above.
https://youtu.be/mwa8vQnGr3I
The following video addresses how to read a pie chart like the one above.
https://youtu.be/mwa8vQnGr3I
Try It
Create a bar graph and a pie chart to illustrate the grades on a history exam below. A: 12 students, B: 19 students, C: 14 students, D: 4 students, F: 5 students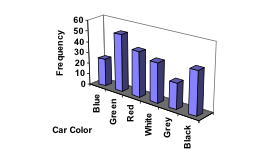 Here is another way that fanciness can lead to trouble. Instead of plain bars, it is tempting to substitute meaningful images. This type of graph is called a pictogram.
Here is another way that fanciness can lead to trouble. Instead of plain bars, it is tempting to substitute meaningful images. This type of graph is called a pictogram.
Pictogram
A pictogram is a statistical graphic in which the size of the picture is intended to represent the frequencies or size of the values being represented.example
 A labor union might produce the graph to the right to show the difference between the average manager salary and the average worker salary.
Looking at the picture, it would be reasonable to guess that the manager salaries is 4 times as large as the worker salaries – the area of the bag looks about 4 times as large. However, the manager salaries are in fact only twice as large as worker salaries, which were reflected in the picture by making the manager bag twice as tall.
This video reviews the two examples of ineffective data representation in more detail.
https://youtu.be/bFwTZNGNLKs
A labor union might produce the graph to the right to show the difference between the average manager salary and the average worker salary.
Looking at the picture, it would be reasonable to guess that the manager salaries is 4 times as large as the worker salaries – the area of the bag looks about 4 times as large. However, the manager salaries are in fact only twice as large as worker salaries, which were reflected in the picture by making the manager bag twice as tall.
This video reviews the two examples of ineffective data representation in more detail.
https://youtu.be/bFwTZNGNLKs
example
Compare the two graphs below showing support for same-sex marriage rights from a poll taken in December 2008[footnote]CNN/Opinion Research Corporation Poll. Dec 19-21, 2008, from http://www.pollingreport.com/civil.htm[/footnote]. The difference in the vertical scale on the first graph suggests a different story than the true differences in percentages; the second graph makes it look like twice as many people oppose marriage rights as support it.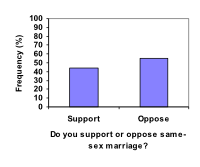

Try It
A poll was taken asking people if they agreed with the positions of the 4 candidates for a county office. Does the pie chart present a good representation of this data? Explain.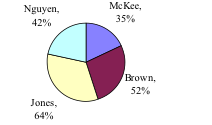
Licenses & Attributions
CC licensed content, Original
- Revision and Adaptation. Provided by: Lumen Learning License: CC BY: Attribution.
CC licensed content, Shared previously
- Presenting Categorical Data Graphically. Authored by: David Lippman. Located at: http://www.opentextbookstore.com/mathinsociety/. License: CC BY-SA: Attribution-ShareAlike.
- Bar graphs for categorical data. Authored by: OCLPhase2's channel. License: CC BY: Attribution.
- Pareto Chart. Authored by: OCLPhase2's channel. License: CC BY: Attribution.
- Creating a pie chart. Authored by: OCLPhase2's channel. License: CC BY: Attribution.
- Reading a pie chart. Authored by: OCLPhase2's channel. License: CC BY: Attribution.
- Bad graphical represenations of data. Authored by: OCLPhase2's channel. License: CC BY: Attribution.
