Union, Intersection, and Complement
Learning Outcomes
- Describe memberships of sets, including the empty set, using proper notation, and decide whether given items are members and determine the cardinality of a given set.
- Describe the relations between sets regarding membership, equality, subset, and proper subset, using proper notation.
- Perform the operations of union, intersection, complement, and difference on sets using proper notation.
- Be able to draw and interpret Venn diagrams of set relations and operations and use Venn diagrams to solve problems.
- Recognize when set theory is applicable to real-life situations, solve real-life problems, and communicate real-life problems and solutions to others.
Union, Intersection, and Complement
The union of two sets contains all the elements contained in either set (or both sets). The union is notated A ⋃ B. More formally, x ∊ A ⋃ B if x ∈ A or x ∈ B (or both) The intersection of two sets contains only the elements that are in both sets. The intersection is notated A ⋂ B. More formally, x ∈ A ⋂ B if x ∈ A and x ∈ B. The complement of a set A contains everything that is not in the set A. The complement is notated A’, or Ac, or sometimes ~A. A universal set is a set that contains all the elements we are interested in. This would have to be defined by the context. A complement is relative to the universal set, so Ac contains all the elements in the universal set that are not in A.Example
- If we were discussing searching for books, the universal set might be all the books in the library.
- If we were grouping your Facebook friends, the universal set would be all your Facebook friends.
- If you were working with sets of numbers, the universal set might be all whole numbers, all integers, or all real numbers
Example
Suppose the universal set is U = all whole numbers from 1 to 9. If A = {1, 2, 4}, then Ac = {3, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9}.Example
Consider the sets: A = {red, green, blue} B = {red, yellow, orange} C = {red, orange, yellow, green, blue, purple} Find the following:- Find A ⋃ B
- Find A ⋂ B
- Find Ac⋂ C
Answer:
- The union contains all the elements in either set: A ⋃ B = {red, green, blue, yellow, orange} Notice we only list red once.
- The intersection contains all the elements in both sets: A ⋂ B = {red}
- Here we’re looking for all the elements that are not in set A and are also in C. Ac ⋂ C = {orange, yellow, purple}
Example
Suppose H = {cat, dog, rabbit, mouse}, F = {dog, cow, duck, pig, rabbit}, and W = {duck, rabbit, deer, frog, mouse}- Find (H ⋂ F) ⋃ W
- Find H ⋂ (F ⋃ W)
- Find (H ⋂ F)c ⋂ W
Answer:
- We start with the intersection: H ⋂ F = {dog, rabbit}. Now we union that result with W: (H ⋂ F) ⋃ W = {dog, duck, rabbit, deer, frog, mouse}
- We start with the union: F ⋃ W = {dog, cow, rabbit, duck, pig, deer, frog, mouse}. Now we intersect that result with H: H ⋂ (F ⋃ W) = {dog, rabbit, mouse}
- We start with the intersection: H ⋂ F = {dog, rabbit}. Now we want to find the elements of W that are not in H ⋂ F. (H ⋂ F)c ⋂ W = {duck, deer, frog, mouse}
Venn Diagrams
To visualize the interaction of sets, John Venn in 1880 thought to use overlapping circles, building on a similar idea used by Leonhard Euler in the 18th century. These illustrations now called Venn Diagrams.Venn Diagram
A Venn diagram represents each set by a circle, usually drawn inside of a containing box representing the universal set. Overlapping areas indicate elements common to both sets. Basic Venn diagrams can illustrate the interaction of two or three sets.Example
Create Venn diagrams to illustrate A ⋃ B, A ⋂ B, and Ac ⋂ B A ⋃ B contains all elements in either set.Answer:
 A ⋂ B contains only those elements in both sets – in the overlap of the circles.
A ⋂ B contains only those elements in both sets – in the overlap of the circles.
 Ac will contain all elements not in the set A. Ac ⋂ B will contain the elements in set B that are not in set A.
Ac will contain all elements not in the set A. Ac ⋂ B will contain the elements in set B that are not in set A.

Example
Use a Venn diagram to illustrate (H ⋂ F)c ⋂ WAnswer:
We’ll start by identifying everything in the set H ⋂ F
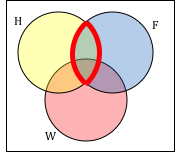 Now, (H ⋂ F)c ⋂ W will contain everything not in the set identified above that is also in set W.
Now, (H ⋂ F)c ⋂ W will contain everything not in the set identified above that is also in set W.

Example
Create an expression to represent the outlined part of the Venn diagram shown.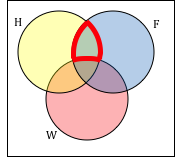
Answer: The elements in the outlined set are in sets H and F, but are not in set W. So we could represent this set as H ⋂ F ⋂ Wc
Try It
Create an expression to represent the outlined portion of the Venn diagram shown.
Licenses & Attributions
CC licensed content, Original
- Revision and Adaptation. Provided by: Lumen Learning License: Public Domain: No Known Copyright.
- Question ID 132343. Provided by: Lumen Learning License: CC BY: Attribution. License terms: IMathAS Community License CC-BY + GPL.
CC licensed content, Shared previously
- Math in Society. Authored by: Open Textbook Store, Transition Math Project, and the Open Course Library. Located at: http://www.opentextbookstore.com/mathinsociety/. License: CC BY-SA: Attribution-ShareAlike.
- Sets: drawing a Venn diagram. Authored by: David Lippman. License: CC BY: Attribution.
- Sets: drawing a Venn diagram. Authored by: David Lippman. License: CC BY: Attribution.
- Question ID 6699. Authored by: Morales,Lawrence. License: CC BY: Attribution. License terms: IMathAS Community License CC-BY + GPL.
- Question ID 125855. Authored by: Bohart, Jenifer. License: CC BY: Attribution. License terms: IMathAS Community License CC-BY + GPL.
